Build secure and cheap Amazon EKS
Build "cheap and secure" Amazon EKS with network policies, cluster encryption and logging
I will outline the steps for setting up an Amazon EKS environment that is both cost-effective and prioritizes security, including the configuration of standard applications.
The Amazon EKS setup should align with the following cost-effectiveness criteria:
- Utilize two Availability Zones (AZs), or a single zone if possible, to reduce payments for cross-AZ traffic
- Spot instances
- Less expensive region -
us-east-1 - Most price efficient EC2 instance type
t4g.medium(2 x CPU, 4GB RAM) using AWS Graviton based on ARM - Use Bottlerocket OS for a minimal operating system, CPU, and memory footprint
- Use Network Load Balancer (NLB) as a most cost efficient + cost optimized load balancer
- Karpenter to enable automatic node scaling that matches the specific resource requirements of pods
The Amazon EKS setup should also meet the following security requirements:
- The Amazon EKS control plane must be encrypted using KMS
- Worker node EBS volumes must be encrypted
- Cluster logging to CloudWatch must be configured
- Network Policies should be enabled where supported
Build Amazon EKS cluster
Requirements
You will need to configure the AWS CLI and set up other necessary secrets and variables.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# AWS Credentials
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
export AWS_SESSION_TOKEN="xxxxxxxx"
export AWS_ROLE_TO_ASSUME="arn:aws:iam::7xxxxxxxxxx7:role/Gixxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxle"
export GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID="10xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxud.apps.googleusercontent.com"
export GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET="GOxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxtw"
If you plan to follow this document and its tasks, you will need to set up a few environment variables, such as:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# AWS Region
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION="${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION:-us-east-1}"
# Hostname / FQDN definitions
export CLUSTER_FQDN="${CLUSTER_FQDN:-k01.k8s.mylabs.dev}"
# Base Domain: k8s.mylabs.dev
export BASE_DOMAIN="${CLUSTER_FQDN#*.}"
# Cluster Name: k01
export CLUSTER_NAME="${CLUSTER_FQDN%%.*}"
export MY_EMAIL="petr.ruzicka@gmail.com"
export TMP_DIR="${TMP_DIR:-${PWD}/tmp}"
export KUBECONFIG="${KUBECONFIG:-${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/kubeconfig-${CLUSTER_NAME}.conf}"
# Tags used to tag the AWS resources
export TAGS="${TAGS:-Owner=${MY_EMAIL},Environment=dev,Cluster=${CLUSTER_FQDN}}"
AWS_ACCOUNT_ID=$(aws sts get-caller-identity --query "Account" --output text) && export AWS_ACCOUNT_ID
mkdir -pv "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}"
Confirm that all essential variables have been properly configured:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
: "${AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID?}"
: "${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION?}"
: "${AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY?}"
: "${AWS_ROLE_TO_ASSUME?}"
: "${GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID?}"
: "${GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET?}"
echo -e "${MY_EMAIL} | ${CLUSTER_NAME} | ${BASE_DOMAIN} | ${CLUSTER_FQDN}\n${TAGS}"
Install the required tools:
You can bypass these procedures if you already have all the essential software installed.
Configure AWS Route 53 Domain delegation
The DNS delegation tasks should be executed as a one-time operation.
Create a DNS zone for the EKS clusters:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
export CLOUDFLARE_EMAIL="petr.ruzicka@gmail.com"
export CLOUDFLARE_API_KEY="1xxxxxxxxx0"
aws route53 create-hosted-zone --output json \
--name "${BASE_DOMAIN}" \
--caller-reference "$(date)" \
--hosted-zone-config="{\"Comment\": \"Created by petr.ruzicka@gmail.com\", \"PrivateZone\": false}" | jq
Utilize your domain registrar to update the nameservers for your zone (e.g., mylabs.dev) to point to the Amazon Route 53 nameservers. Here’s how to discover the required Route 53 nameservers:
1
2
3
4
NEW_ZONE_ID=$(aws route53 list-hosted-zones --query "HostedZones[?Name==\`${BASE_DOMAIN}.\`].Id" --output text)
NEW_ZONE_NS=$(aws route53 get-hosted-zone --output json --id "${NEW_ZONE_ID}" --query "DelegationSet.NameServers")
NEW_ZONE_NS1=$(echo "${NEW_ZONE_NS}" | jq -r ".[0]")
NEW_ZONE_NS2=$(echo "${NEW_ZONE_NS}" | jq -r ".[1]")
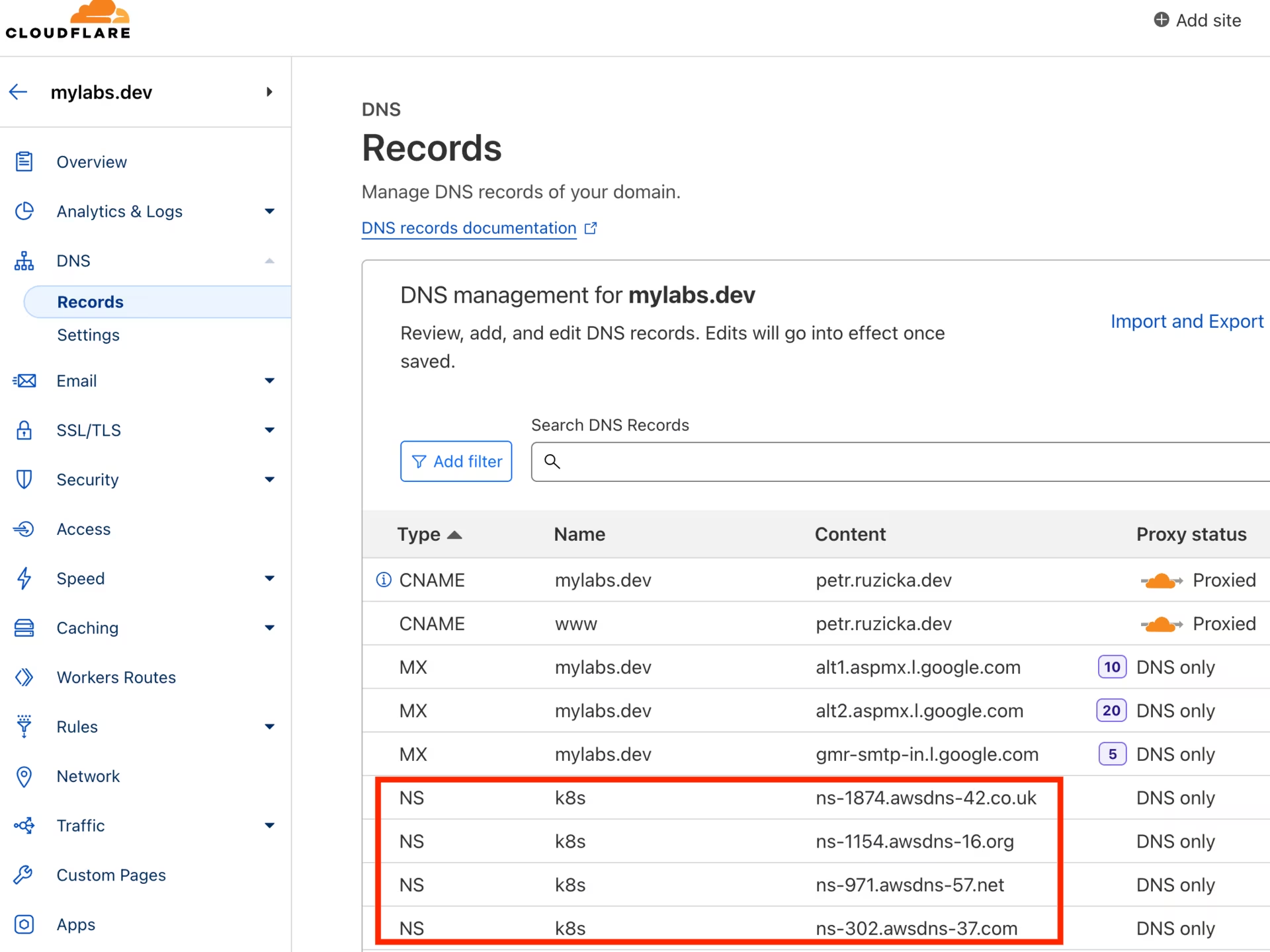
Establish the NS record in k8s.mylabs.dev (your BASE_DOMAIN) for proper zone delegation. This operation’s specifics may vary based on your domain registrar; I use Cloudflare and employ Ansible for automation:
1
2
ansible -m cloudflare_dns -c local -i "localhost," localhost -a "zone=mylabs.dev record=${BASE_DOMAIN} type=NS value=${NEW_ZONE_NS1} solo=true proxied=no account_email=${CLOUDFLARE_EMAIL} account_api_token=${CLOUDFLARE_API_KEY}"
ansible -m cloudflare_dns -c local -i "localhost," localhost -a "zone=mylabs.dev record=${BASE_DOMAIN} type=NS value=${NEW_ZONE_NS2} solo=false proxied=no account_email=${CLOUDFLARE_EMAIL} account_api_token=${CLOUDFLARE_API_KEY}"
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
localhost | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"result": {
"record": {
"content": "ns-885.awsdns-46.net",
"created_on": "2020-11-13T06:25:32.18642Z",
"id": "dxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxb",
"locked": false,
"meta": {
"auto_added": false,
"managed_by_apps": false,
"managed_by_argo_tunnel": false,
"source": "primary"
},
"modified_on": "2020-11-13T06:25:32.18642Z",
"name": "k8s.mylabs.dev",
"proxiable": false,
"proxied": false,
"ttl": 1,
"type": "NS",
"zone_id": "2xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxe",
"zone_name": "mylabs.dev"
}
}
}
localhost | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"result": {
"record": {
"content": "ns-1692.awsdns-19.co.uk",
"created_on": "2020-11-13T06:25:37.605605Z",
"id": "9xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxb",
"locked": false,
"meta": {
"auto_added": false,
"managed_by_apps": false,
"managed_by_argo_tunnel": false,
"source": "primary"
},
"modified_on": "2020-11-13T06:25:37.605605Z",
"name": "k8s.mylabs.dev",
"proxiable": false,
"proxied": false,
"ttl": 1,
"type": "NS",
"zone_id": "2xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxe",
"zone_name": "mylabs.dev"
}
}
}
Create Route53 zone and KMS key
Generate a CloudFormation template that defines an Amazon Route 53 zone and an AWS Key Management Service (KMS) key.
Add the new domain CLUSTER_FQDN to Route 53, and set up DNS delegation from the BASE_DOMAIN.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
tee "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/aws-cf-route53-kms.yml" << \EOF
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: Route53 entries and KMS key
Parameters:
BaseDomain:
Description: "Base domain where cluster domains + their subdomains will live - Ex: k8s.mylabs.dev"
Type: String
ClusterFQDN:
Description: "Cluster FQDN (domain for all applications) - Ex: k01.k8s.mylabs.dev"
Type: String
ClusterName:
Description: "Cluster Name - Ex: k01"
Type: String
Resources:
HostedZone:
Type: AWS::Route53::HostedZone
Properties:
Name: !Ref ClusterFQDN
RecordSet:
Type: AWS::Route53::RecordSet
Properties:
HostedZoneName: !Sub "${BaseDomain}."
Name: !Ref ClusterFQDN
Type: NS
TTL: 60
ResourceRecords: !GetAtt HostedZone.NameServers
KMSAlias:
Type: AWS::KMS::Alias
Properties:
AliasName: !Sub "alias/eks-${ClusterName}"
TargetKeyId: !Ref KMSKey
KMSKey:
Type: AWS::KMS::Key
Properties:
Description: !Sub "KMS key for ${ClusterName} Amazon EKS"
EnableKeyRotation: true
PendingWindowInDays: 7
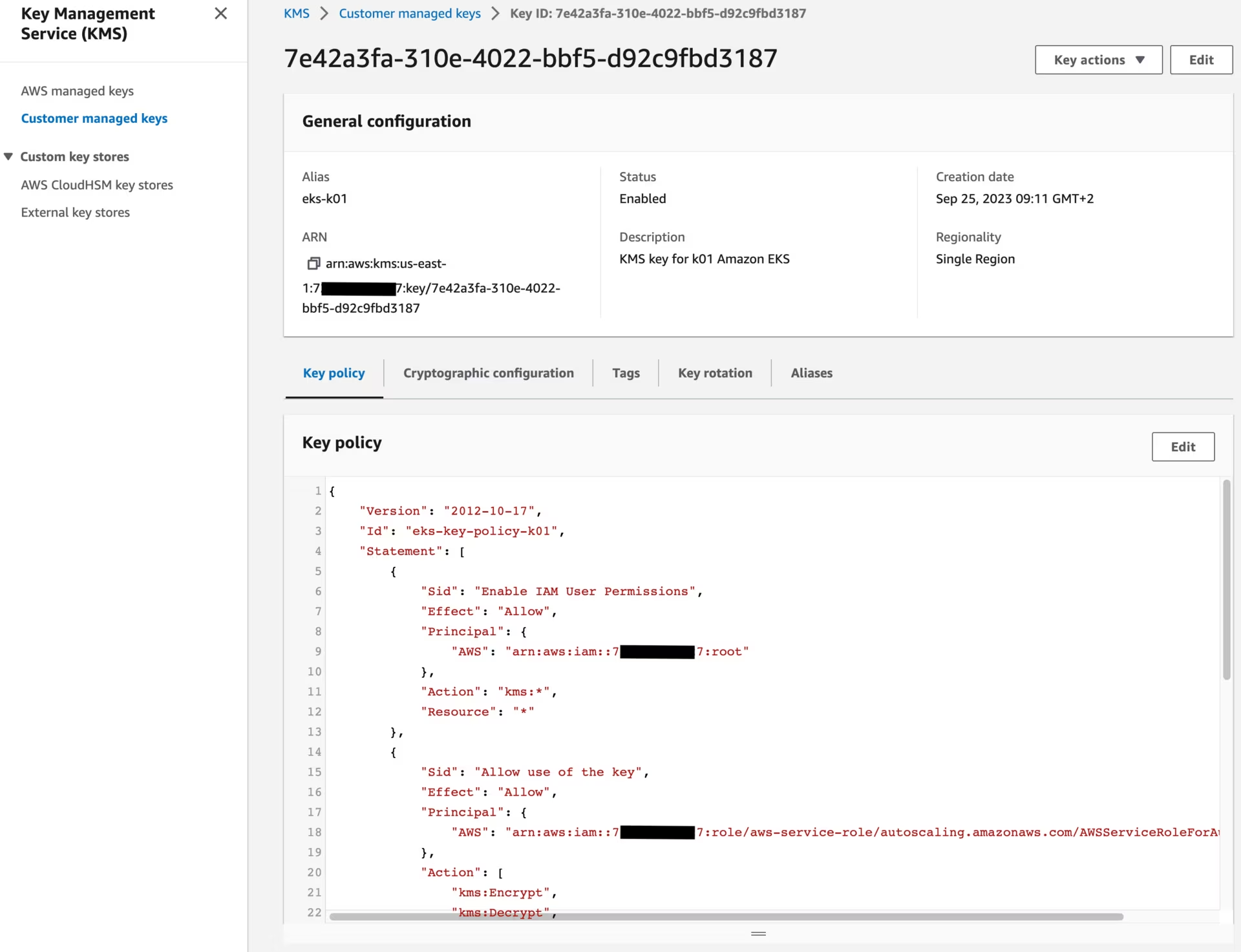
KeyPolicy:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Id: !Sub "eks-key-policy-${ClusterName}"
Statement:
- Sid: Enable IAM User Permissions
Effect: Allow
Principal:
AWS:
- !Sub "arn:aws:iam::${AWS::AccountId}:root"
Action: kms:*
Resource: "*"
- Sid: Allow use of the key
Effect: Allow
Principal:
AWS:
- !Sub "arn:aws:iam::${AWS::AccountId}:role/aws-service-role/autoscaling.amazonaws.com/AWSServiceRoleForAutoScaling"
# The following roles needs to be enabled after the EKS cluster is created
# aws-ebs-csi-driver + Karpenter should be able to use the KMS key
# - !Sub "arn:aws:iam::${AWS::AccountId}:role/eksctl-${ClusterName}-irsa-aws-ebs-csi-driver"
# - !Sub "arn:aws:iam::${AWS::AccountId}:role/eksctl-${ClusterName}-iamservice-role"
Action:
- kms:Encrypt
- kms:Decrypt
- kms:ReEncrypt*
- kms:GenerateDataKey*
- kms:DescribeKey
Resource: "*"
- Sid: Allow attachment of persistent resources
Effect: Allow
Principal:
AWS:
- !Sub "arn:aws:iam::${AWS::AccountId}:role/aws-service-role/autoscaling.amazonaws.com/AWSServiceRoleForAutoScaling"
# - !Sub "arn:aws:iam::${AWS::AccountId}:role/eksctl-${ClusterName}-irsa-aws-ebs-csi-driver"
# - !Sub "arn:aws:iam::${AWS::AccountId}:role/eksctl-${ClusterName}-iamservice-role"
Action:
- kms:CreateGrant
Resource: "*"
Condition:
Bool:
kms:GrantIsForAWSResource: true
Outputs:
KMSKeyArn:
Description: The ARN of the created KMS Key to encrypt EKS related services
Value: !GetAtt KMSKey.Arn
Export:
Name:
Fn::Sub: "${AWS::StackName}-KMSKeyArn"
KMSKeyId:
Description: The ID of the created KMS Key to encrypt EKS related services
Value: !Ref KMSKey
Export:
Name:
Fn::Sub: "${AWS::StackName}-KMSKeyId"
EOF
if [[ $(aws cloudformation list-stacks --stack-status-filter CREATE_COMPLETE --query "StackSummaries[?starts_with(StackName, \`${CLUSTER_NAME}-route53-kms\`) == \`true\`].StackName" --output text) == "" ]]; then
# shellcheck disable=SC2001
eval aws cloudformation deploy --capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--parameter-overrides "BaseDomain=${BASE_DOMAIN} ClusterFQDN=${CLUSTER_FQDN} ClusterName=${CLUSTER_NAME}" \
--stack-name "${CLUSTER_NAME}-route53-kms" --template-file "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/aws-cf-route53-kms.yml" --tags "${TAGS//,/ }"
fi
# shellcheck disable=SC2016
AWS_CLOUDFORMATION_DETAILS=$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name "${CLUSTER_NAME}-route53-kms" --query 'Stacks[0].Outputs[? OutputKey==`KMSKeyArn` || OutputKey==`KMSKeyId`].{OutputKey:OutputKey,OutputValue:OutputValue}')
AWS_KMS_KEY_ARN=$(echo "${AWS_CLOUDFORMATION_DETAILS}" | jq -r ".[] | select(.OutputKey==\"KMSKeyArn\") .OutputValue")
AWS_KMS_KEY_ID=$(echo "${AWS_CLOUDFORMATION_DETAILS}" | jq -r ".[] | select(.OutputKey==\"KMSKeyId\") .OutputValue")
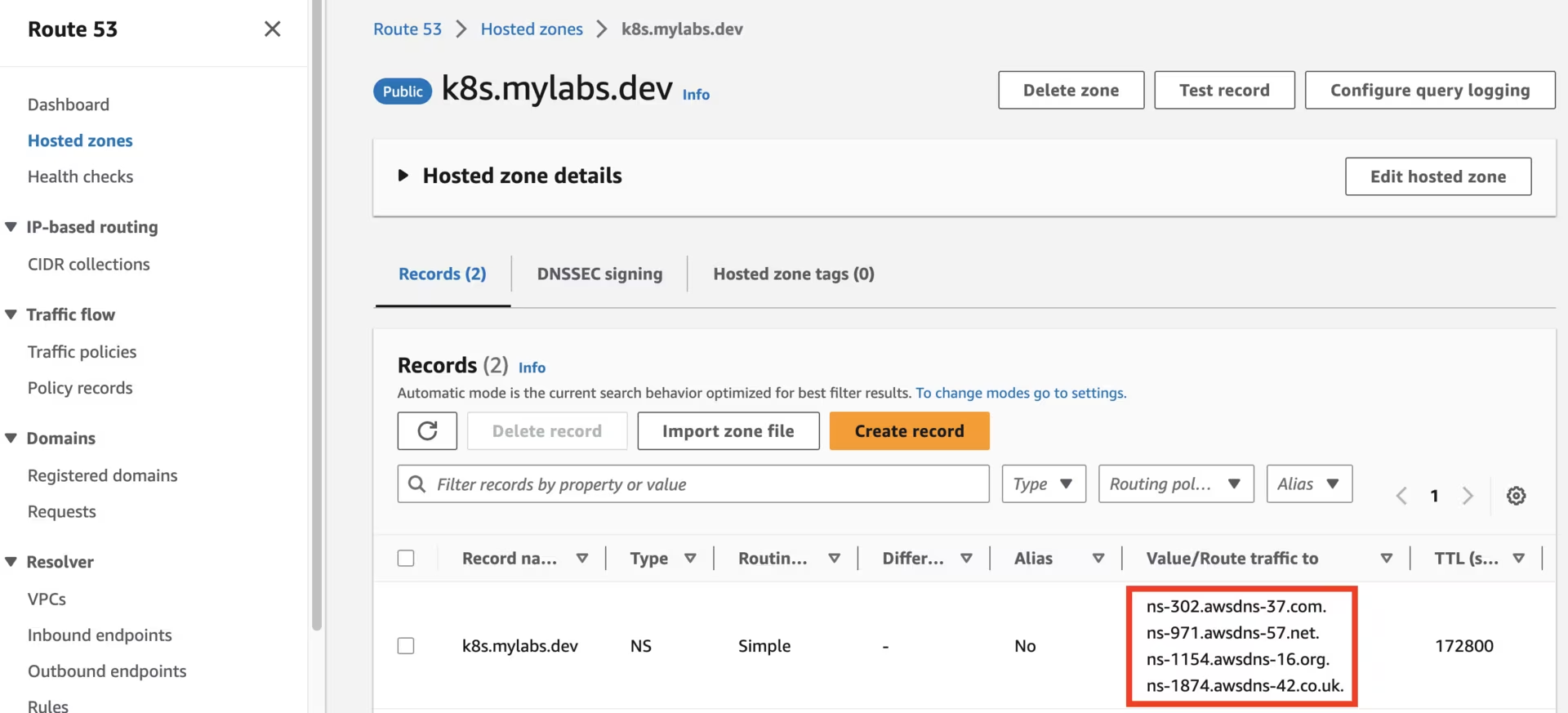
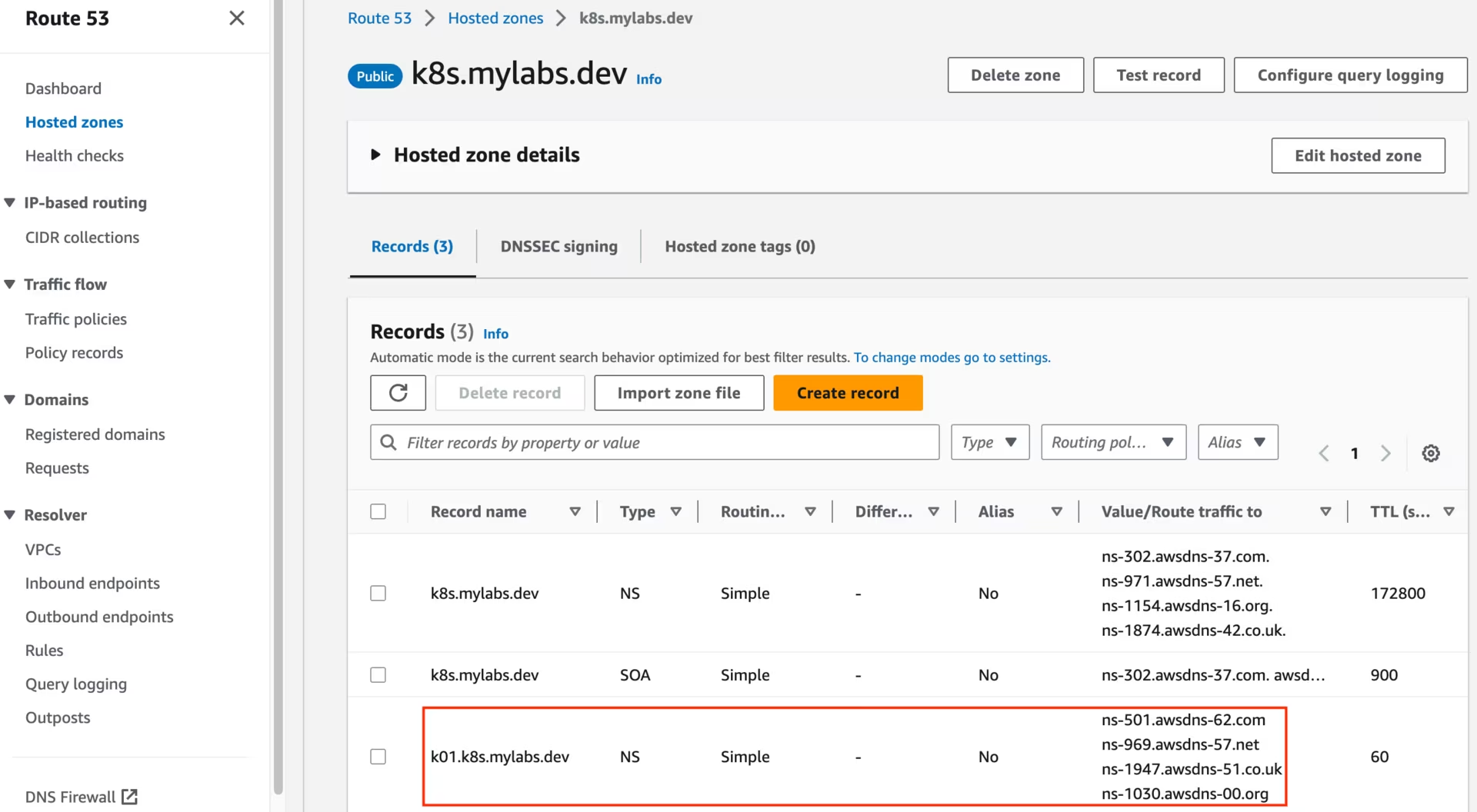
After running the CloudFormation stack, you should see the following Route53 zones:
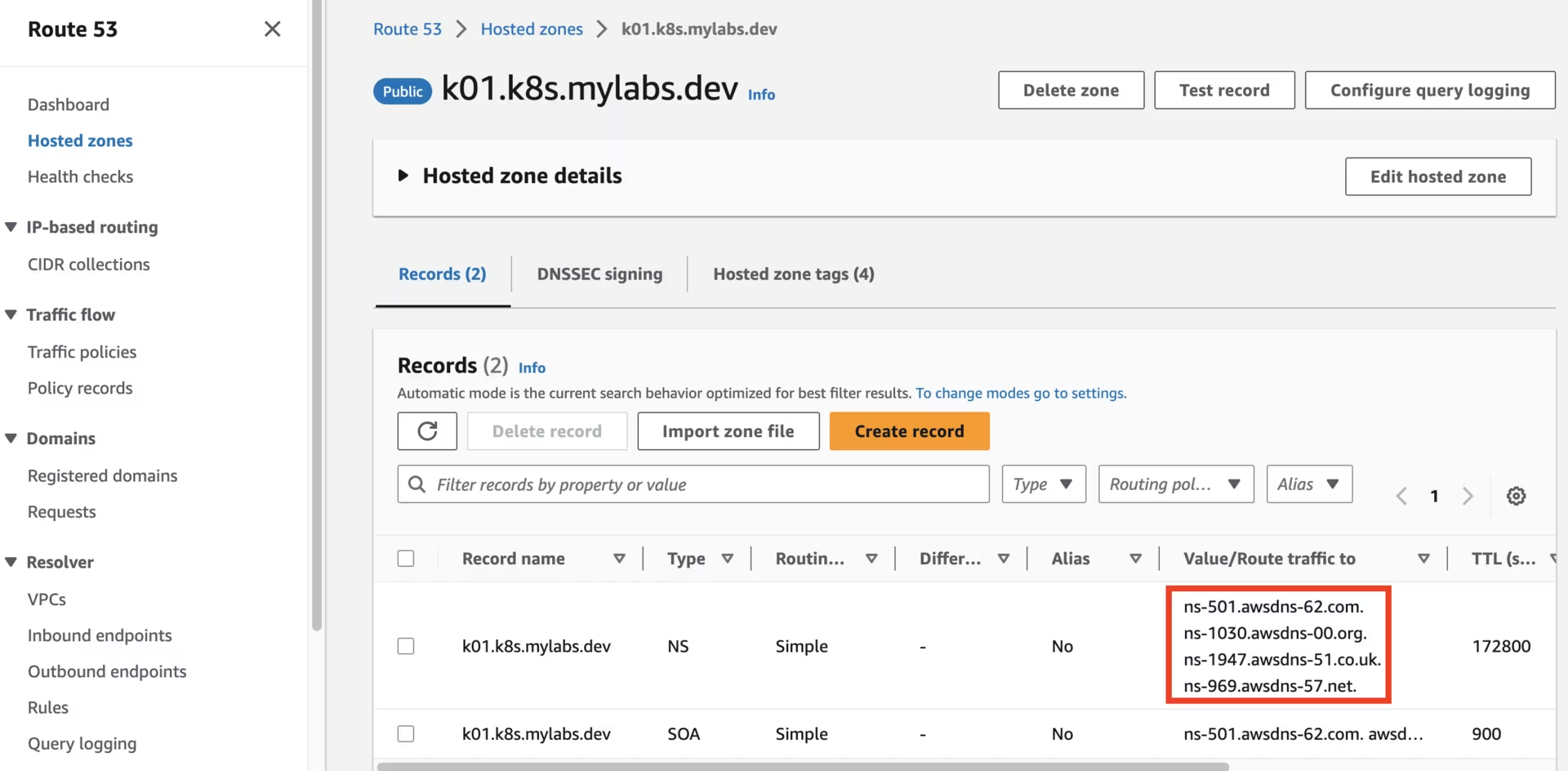 Route53 k01.k8s.mylabs.dev zone
Route53 k01.k8s.mylabs.dev zone
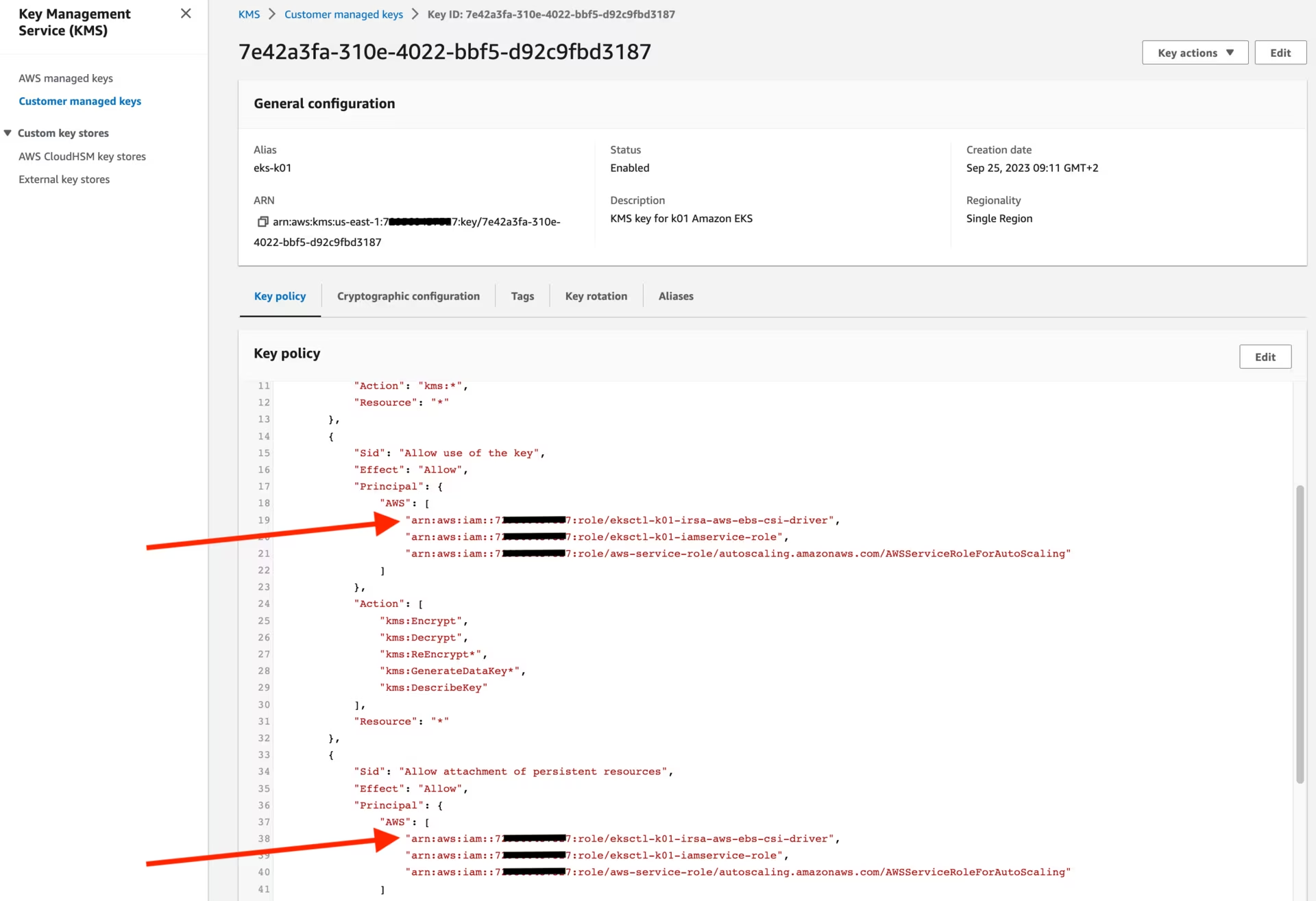
You should also see the following KMS key:
Create Amazon EKS
I will use eksctl to create the Amazon EKS cluster.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
tee "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/eksctl-${CLUSTER_NAME}.yml" << EOF
apiVersion: eksctl.io/v1alpha5
kind: ClusterConfig
metadata:
name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
region: ${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}
tags:
karpenter.sh/discovery: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
$(echo "${TAGS}" | sed "s/,/\\n /g; s/=/: /g")
availabilityZones:
- ${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}a
- ${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}b
iam:
withOIDC: true
serviceAccounts:
- metadata:
name: aws-for-fluent-bit
namespace: aws-for-fluent-bit
attachPolicyARNs:
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/CloudWatchAgentServerPolicy
roleName: eksctl-${CLUSTER_NAME}-irsa-aws-for-fluent-bit
- metadata:
name: ebs-csi-controller-sa
namespace: aws-ebs-csi-driver
wellKnownPolicies:
ebsCSIController: true
roleName: eksctl-${CLUSTER_NAME}-irsa-aws-ebs-csi-driver
- metadata:
name: cert-manager
namespace: cert-manager
wellKnownPolicies:
certManager: true
roleName: eksctl-${CLUSTER_NAME}-irsa-cert-manager
- metadata:
name: external-dns
namespace: external-dns
wellKnownPolicies:
externalDNS: true
roleName: eksctl-${CLUSTER_NAME}-irsa-external-dns
# Allow users which are consuming the AWS_ROLE_TO_ASSUME to access the EKS
iamIdentityMappings:
- arn: arn:aws:iam::${AWS_ACCOUNT_ID}:role/admin
groups:
- system:masters
username: admin
karpenter:
# renovate: datasource=github-tags depName=aws/karpenter extractVersion=^(?<version>.*)$
version: v0.31.4
createServiceAccount: true
withSpotInterruptionQueue: true
addons:
- name: vpc-cni
version: latest
configurationValues: |-
enableNetworkPolicy: "true"
env:
ENABLE_PREFIX_DELEGATION: "true"
- name: kube-proxy
- name: coredns
managedNodeGroups:
- name: mng01-ng
amiFamily: Bottlerocket
# Minimal instance type for running add-ons + karpenter - ARM t4g.medium: 4.0 GiB, 2 vCPUs - 0.0336 hourly
# Minimal instance type for running add-ons + karpenter - X86 t3a.medium: 4.0 GiB, 2 vCPUs - 0.0336 hourly
instanceType: t4g.medium
# Due to karpenter we need 2 instances
desiredCapacity: 2
availabilityZones:
- ${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}a
minSize: 2
maxSize: 5
volumeSize: 20
disablePodIMDS: true
volumeEncrypted: true
volumeKmsKeyID: ${AWS_KMS_KEY_ID}
maxPodsPerNode: 110
privateNetworking: true
bottlerocket:
settings:
kubernetes:
seccomp-default: true
secretsEncryption:
keyARN: ${AWS_KMS_KEY_ARN}
cloudWatch:
clusterLogging:
logRetentionInDays: 1
enableTypes:
- all
EOF
Get the kubeconfig file to access the cluster:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
if [[ ! -s "${KUBECONFIG}" ]]; then
if ! eksctl get clusters --name="${CLUSTER_NAME}" &> /dev/null; then
eksctl create cluster --config-file "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/eksctl-${CLUSTER_NAME}.yml" --kubeconfig "${KUBECONFIG}"
# Add roles created by eksctl to the KMS policy to allow aws-ebs-csi-driver work with encrypted EBS volumes
sed -i "s@# \(- \!Sub \"arn:aws:iam::\${AWS::AccountId}:role/eksctl-\${ClusterName}.*\)@\1@" "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/aws-cf-route53-kms.yml"
eval aws cloudformation update-stack \
--parameters "ParameterKey=BaseDomain,ParameterValue=${BASE_DOMAIN} ParameterKey=ClusterFQDN,ParameterValue=${CLUSTER_FQDN} ParameterKey=ClusterName,ParameterValue=${CLUSTER_NAME}" \
--stack-name "${CLUSTER_NAME}-route53-kms" --template-body "file://${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/aws-cf-route53-kms.yml"
else
eksctl utils write-kubeconfig --cluster="${CLUSTER_NAME}" --kubeconfig "${KUBECONFIG}"
fi
fi
aws eks update-kubeconfig --name="${CLUSTER_NAME}"
The sed command used earlier modified the aws-cf-route53-kms.yml file by incorporating the newly established IAM roles (eksctl-k01-irsa-aws-ebs-csi-driver and eksctl-k01-iamservice-role), enabling them to utilize the KMS key.
1
2
3
AWS_VPC_ID=$(aws ec2 describe-vpcs --filters "Name=tag:alpha.eksctl.io/cluster-name,Values=${CLUSTER_NAME}" --query 'Vpcs[*].VpcId' --output text)
AWS_SECURITY_GROUP_ID=$(aws ec2 describe-security-groups --filters "Name=vpc-id,Values=${AWS_VPC_ID}" "Name=group-name,Values=default" --query 'SecurityGroups[*].GroupId' --output text)
AWS_NACL_ID=$(aws ec2 describe-network-acls --filters "Name=vpc-id,Values=${AWS_VPC_ID}" --query 'NetworkAcls[*].NetworkAclId' --output text)
Enhance the security posture of the EKS cluster by addressing the following concerns:
The default security group should have no rules configured:
1 2
aws ec2 revoke-security-group-egress --group-id "${AWS_SECURITY_GROUP_ID}" --protocol all --port all --cidr 0.0.0.0/0 | jq || true aws ec2 revoke-security-group-ingress --group-id "${AWS_SECURITY_GROUP_ID}" --protocol all --port all --source-group "${AWS_SECURITY_GROUP_ID}" | jq || true
The VPC NACL allows unrestricted SSH access, and the VPC NACL allows unrestricted RDP access:
1 2
aws ec2 create-network-acl-entry --network-acl-id "${AWS_NACL_ID}" --ingress --rule-number 1 --protocol tcp --port-range "From=22,To=22" --cidr-block 0.0.0.0/0 --rule-action Deny aws ec2 create-network-acl-entry --network-acl-id "${AWS_NACL_ID}" --ingress --rule-number 2 --protocol tcp --port-range "From=3389,To=3389" --cidr-block 0.0.0.0/0 --rule-action Deny
The namespace does not have a PSS level assigned:
1
kubectl label namespace default pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce=baseline
Karpenter
Karpenter is a Kubernetes node autoscaler built for flexibility, performance, and simplicity.
Configure Karpenter by applying the following provisioner definition:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
tee "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/k8s-karpenter-provisioner.yml" << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: karpenter.sh/v1alpha5
kind: Provisioner
metadata:
name: default
spec:
consolidation:
enabled: true
requirements:
- key: karpenter.sh/capacity-type
operator: In
values: ["spot", "on-demand"]
- key: kubernetes.io/arch
operator: In
values: ["amd64", "arm64"]
- key: "topology.kubernetes.io/zone"
operator: In
values: ["${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}a"]
- key: karpenter.k8s.aws/instance-family
operator: In
values: ["t3a", "t4g"]
kubeletConfiguration:
maxPods: 110
# Resource limits constrain the total size of the cluster.
# Limits prevent Karpenter from creating new instances once the limit is exceeded.
limits:
resources:
cpu: 8
memory: 32Gi
providerRef:
name: default
# Labels are arbitrary key-values that are applied to all nodes
labels:
managedBy: karpenter
provisioner: default
---
apiVersion: karpenter.k8s.aws/v1alpha1
kind: AWSNodeTemplate
metadata:
name: default
spec:
amiFamily: Bottlerocket
subnetSelector:
karpenter.sh/discovery: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
securityGroupSelector:
karpenter.sh/discovery: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
blockDeviceMappings:
- deviceName: /dev/xvda
ebs:
volumeSize: 2Gi
volumeType: gp3
encrypted: true
kmsKeyID: ${AWS_KMS_KEY_ARN}
- deviceName: /dev/xvdb
ebs:
volumeSize: 20Gi
volumeType: gp3
encrypted: true
kmsKeyID: ${AWS_KMS_KEY_ARN}
tags:
KarpenerProvisionerName: "default"
Name: "${CLUSTER_NAME}-karpenter"
$(echo "${TAGS}" | sed "s/,/\\n /g; s/=/: /g")
EOF
aws-node-termination-handler
The AWS Node Termination Handler gracefully handles EC2 instance shutdowns within Kubernetes.
It is not needed when using EKS managed node groups, as discussed in Use with managed node groups.
snapshot-controller
Install the Volume Snapshot Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs):
1
kubectl apply --kustomize 'https://github.com/kubernetes-csi/external-snapshotter//client/config/crd/?ref=v8.1.0'
Install the volume snapshot controller snapshot-controller Helm chart and modify its default values:
1
2
3
4
5
6
# renovate: datasource=helm depName=snapshot-controller registryUrl=https://piraeus.io/helm-charts/
SNAPSHOT_CONTROLLER_HELM_CHART_VERSION="2.2.0"
helm repo add --force-update piraeus-charts https://piraeus.io/helm-charts/
helm upgrade --wait --install --version "${SNAPSHOT_CONTROLLER_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace snapshot-controller --create-namespace snapshot-controller piraeus-charts/snapshot-controller
kubectl label namespace snapshot-controller pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce=baseline
aws-ebs-csi-driver
The Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) Container Storage Interface (CSI) Driver provides a CSI interface used by Container Orchestrators to manage the lifecycle of Amazon EBS volumes.
(The ebs-csi-controller-sa ServiceAccount was created by eksctl) Install the Amazon EBS CSI Driver aws-ebs-csi-driver Helm chart and modify its default values:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
# renovate: datasource=helm depName=aws-ebs-csi-driver registryUrl=https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/aws-ebs-csi-driver
AWS_EBS_CSI_DRIVER_HELM_CHART_VERSION="2.28.1"
helm repo add --force-update aws-ebs-csi-driver https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/aws-ebs-csi-driver
tee "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-aws-ebs-csi-driver.yml" << EOF
controller:
enableMetrics: false
serviceMonitor:
forceEnable: true
k8sTagClusterId: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
extraVolumeTags:
"eks:cluster-name": ${CLUSTER_NAME}
$(echo "${TAGS}" | sed "s/,/\\n /g; s/=/: /g")
serviceAccount:
create: false
name: ebs-csi-controller-sa
region: ${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}
node:
securityContext:
# The node pod must be run as root to bind to the registration/driver sockets
runAsNonRoot: false
storageClasses:
- name: gp3
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"
parameters:
encrypted: "true"
kmskeyid: ${AWS_KMS_KEY_ARN}
volumeSnapshotClasses:
- name: ebs-vsc
annotations:
snapshot.storage.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"
deletionPolicy: Delete
EOF
helm upgrade --install --version "${AWS_EBS_CSI_DRIVER_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace aws-ebs-csi-driver --values "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-aws-ebs-csi-driver.yml" aws-ebs-csi-driver aws-ebs-csi-driver/aws-ebs-csi-driver
Delete the gp2 StorageClass, as gp3 will be used instead:
1
kubectl delete storageclass gp2 || true
mailpit
Mailpit will be used to receive email alerts from the Prometheus.
Install mailpit helm chart and modify the default values:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# renovate: datasource=helm depName=mailpit registryUrl=https://jouve.github.io/charts/
MAILPIT_HELM_CHART_VERSION="0.14.0"
helm repo add --force-update jouve https://jouve.github.io/charts/
tee "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-mailpit.yml" << EOF
ingress:
enabled: true
annotations:
forecastle.stakater.com/expose: "true"
forecastle.stakater.com/icon: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sj26/mailcatcher/main/assets/images/logo_large.png
forecastle.stakater.com/appName: Mailpit
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-url: https://oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_FQDN}/oauth2/auth
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-signin: https://oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_FQDN}/oauth2/start?rd=\$scheme://\$host\$request_uri
ingressClassName: nginx
hostname: mailpit.${CLUSTER_FQDN}
EOF
helm upgrade --install --version "${MAILPIT_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace mailpit --create-namespace --values "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-mailpit.yml" mailpit jouve/mailpit
kubectl label namespace mailpit pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce=baseline
kube-prometheus-stack
Prometheus should be one of the initial applications installed on the Kubernetes cluster because numerous Kubernetes services and applications can export metrics to it.
The kube-prometheus-stack is a collection of Kubernetes manifests, Grafana dashboards, and Prometheus rules. It’s combined with documentation and scripts to provide easy-to-operate, end-to-end Kubernetes cluster monitoring with Prometheus using the Prometheus Operator.
Install the kube-prometheus-stack Helm chart and modify its default values:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
# renovate: datasource=helm depName=kube-prometheus-stack registryUrl=https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
KUBE_PROMETHEUS_STACK_HELM_CHART_VERSION="56.6.2"
helm repo add --force-update prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
tee "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-kube-prometheus-stack.yml" << EOF
defaultRules:
rules:
etcd: false
kubernetesSystem: false
kubeScheduler: false
alertmanager:
config:
global:
smtp_smarthost: "mailpit-smtp.mailpit.svc.cluster.local:25"
smtp_from: "alertmanager@${CLUSTER_FQDN}"
route:
group_by: ["alertname", "job"]
receiver: email
routes:
- receiver: 'null'
matchers:
- alertname =~ "InfoInhibitor|Watchdog"
- receiver: email
matchers:
- severity =~ "warning|critical"
receivers:
- name: email
email_configs:
- to: "notification@${CLUSTER_FQDN}"
require_tls: false
ingress:
enabled: true
ingressClassName: nginx
annotations:
forecastle.stakater.com/expose: "true"
forecastle.stakater.com/icon: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stakater/ForecastleIcons/master/alert-manager.png
forecastle.stakater.com/appName: Alert Manager
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-url: https://oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_FQDN}/oauth2/auth
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-signin: https://oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_FQDN}/oauth2/start?rd=\$scheme://\$host\$request_uri
hosts:
- alertmanager.${CLUSTER_FQDN}
paths: ["/"]
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
tls:
- hosts:
- alertmanager.${CLUSTER_FQDN}
# https://github.com/grafana/helm-charts/blob/main/charts/grafana/values.yaml
grafana:
defaultDashboardsEnabled: false
serviceMonitor:
enabled: true
ingress:
enabled: true
ingressClassName: nginx
annotations:
forecastle.stakater.com/expose: "true"
forecastle.stakater.com/icon: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stakater/ForecastleIcons/master/grafana.png
forecastle.stakater.com/appName: Grafana
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-url: https://oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_FQDN}/oauth2/auth
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-signin: https://oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_FQDN}/oauth2/start?rd=\$scheme://\$host\$request_uri
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/configuration-snippet: |
auth_request_set \$email \$upstream_http_x_auth_request_email;
proxy_set_header X-Email \$email;
hosts:
- grafana.${CLUSTER_FQDN}
paths: ["/"]
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
tls:
- hosts:
- grafana.${CLUSTER_FQDN}
datasources:
datasource.yaml:
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: Prometheus
type: prometheus
url: http://kube-prometheus-stack-prometheus.kube-prometheus-stack:9090/
access: proxy
isDefault: true
dashboardProviders:
dashboardproviders.yaml:
apiVersion: 1
providers:
- name: "default"
orgId: 1
folder: ""
type: file
disableDeletion: false
editable: true
options:
path: /var/lib/grafana/dashboards/default
dashboards:
default:
1860-node-exporter-full:
# renovate: depName="Node Exporter Full"
gnetId: 1860
revision: 36
datasource: Prometheus
3662-prometheus-2-0-overview:
# renovate: depName="Prometheus 2.0 Overview"
gnetId: 3662
revision: 2
datasource: Prometheus
9852-stians-disk-graphs:
# renovate: depName="node-exporter disk graphs"
gnetId: 9852
revision: 1
datasource: Prometheus
12006-kubernetes-apiserver:
# renovate: depName="Kubernetes apiserver"
gnetId: 12006
revision: 1
datasource: Prometheus
9614-nginx-ingress-controller:
# renovate: depName="NGINX Ingress controller"
gnetId: 9614
revision: 1
datasource: Prometheus
11875-kubernetes-ingress-nginx-eks:
# renovate: depName="Kubernetes Ingress Nginx - EKS"
gnetId: 11875
revision: 1
datasource: Prometheus
15038-external-dns:
# renovate: depName="External-dns"
gnetId: 15038
revision: 3
datasource: Prometheus
14314-kubernetes-nginx-ingress-controller-nextgen-devops-nirvana:
# renovate: depName="Kubernetes Nginx Ingress Prometheus NextGen"
gnetId: 14314
revision: 2
datasource: Prometheus
13473-portefaix-kubernetes-cluster-overview:
# renovate: depName="Portefaix / Kubernetes cluster Overview"
gnetId: 13473
revision: 2
datasource: Prometheus
# https://grafana.com/orgs/imrtfm/dashboards - https://github.com/dotdc/grafana-dashboards-kubernetes
15760-kubernetes-views-pods:
# renovate: depName="Kubernetes / Views / Pods"
gnetId: 15760
revision: 26
datasource: Prometheus
15757-kubernetes-views-global:
# renovate: depName="Kubernetes / Views / Global"
gnetId: 15757
revision: 37
datasource: Prometheus
15758-kubernetes-views-namespaces:
# renovate: depName="Kubernetes / Views / Namespaces"
gnetId: 15758
revision: 34
datasource: Prometheus
15759-kubernetes-views-nodes:
# renovate: depName="Kubernetes / Views / Nodes"
gnetId: 15759
revision: 29
datasource: Prometheus
15761-kubernetes-system-api-server:
# renovate: depName="Kubernetes / System / API Server"
gnetId: 15761
revision: 16
datasource: Prometheus
15762-kubernetes-system-coredns:
# renovate: depName="Kubernetes / System / CoreDNS"
gnetId: 15762
revision: 17
datasource: Prometheus
19105-prometheus:
# renovate: depName="Prometheus"
gnetId: 19105
revision: 3
datasource: Prometheus
16237-cluster-capacity:
# renovate: depName="Cluster Capacity (Karpenter)"
gnetId: 16237
revision: 1
datasource: Prometheus
16236-pod-statistic:
# renovate: depName="Pod Statistic (Karpenter)"
gnetId: 16236
revision: 1
datasource: Prometheus
19268-prometheus:
# renovate: depName="Prometheus All Metrics"
gnetId: 19268
revision: 1
datasource: Prometheus
18855-fluent-bit:
# renovate: depName="Fluent Bit"
gnetId: 18855
revision: 1
datasource: Prometheus
grafana.ini:
analytics:
check_for_updates: false
server:
root_url: https://grafana.${CLUSTER_FQDN}
# Use oauth2-proxy instead of default Grafana Oauth
auth.basic:
enabled: false
auth.proxy:
enabled: true
header_name: X-Email
header_property: email
users:
auto_assign_org_role: Admin
smtp:
enabled: true
host: "mailpit-smtp.mailpit.svc.cluster.local:25"
from_address: grafana@${CLUSTER_FQDN}
networkPolicy:
enabled: true
kubeControllerManager:
enabled: false
kubeEtcd:
enabled: false
kubeScheduler:
enabled: false
kubeProxy:
enabled: false
kube-state-metrics:
networkPolicy:
enabled: true
selfMonitor:
enabled: true
prometheus-node-exporter:
networkPolicy:
enabled: true
prometheusOperator:
networkPolicy:
enabled: true
prometheus:
networkPolicy:
enabled: false
ingress:
enabled: true
ingressClassName: nginx
annotations:
forecastle.stakater.com/expose: "true"
forecastle.stakater.com/icon: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cncf/artwork/master/projects/prometheus/icon/color/prometheus-icon-color.svg
forecastle.stakater.com/appName: Prometheus
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-url: https://oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_FQDN}/oauth2/auth
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-signin: https://oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_FQDN}/oauth2/start?rd=\$scheme://\$host\$request_uri
paths: ["/"]
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
hosts:
- prometheus.${CLUSTER_FQDN}
tls:
- hosts:
- prometheus.${CLUSTER_FQDN}
prometheusSpec:
externalLabels:
cluster: ${CLUSTER_FQDN}
externalUrl: https://prometheus.${CLUSTER_FQDN}
ruleSelectorNilUsesHelmValues: false
serviceMonitorSelectorNilUsesHelmValues: false
podMonitorSelectorNilUsesHelmValues: false
retentionSize: 1GB
walCompression: true
storageSpec:
volumeClaimTemplate:
spec:
storageClassName: gp3
accessModes: ["ReadWriteOnce"]
resources:
requests:
storage: 2Gi
EOF
helm upgrade --install --version "${KUBE_PROMETHEUS_STACK_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace kube-prometheus-stack --create-namespace --values "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-kube-prometheus-stack.yml" kube-prometheus-stack prometheus-community/kube-prometheus-stack
karpenter
Karpenter automatically launches appropriately sized compute resources to handle your cluster’s applications.
Customize the Karpenter default installation by upgrading its Helm chart and modifying the default values:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# renovate: datasource=github-tags depName=aws/karpenter extractVersion=^(?<version>.*)$
KARPENTER_HELM_CHART_VERSION="v0.31.4"
tee "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-karpenter.yml" << EOF
replicas: 1
serviceMonitor:
enabled: true
settings:
aws:
enablePodENI: true
reservedENIs: "1"
EOF
helm upgrade --install --version "${KARPENTER_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace karpenter --reuse-values --values "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-karpenter.yml" karpenter oci://public.ecr.aws/karpenter/karpenter
kubectl label namespace karpenter pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce=baseline
aws-for-fluent-bit
Fluent Bit is an open-source log processor and forwarder that allows you to collect data, like metrics and logs, from different sources, enrich it with filters, and send it to multiple destinations.
Install the aws-for-fluent-bit Helm chart and modify its default values:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# renovate: datasource=helm depName=aws-for-fluent-bit registryUrl=https://aws.github.io/eks-charts
AWS_FOR_FLUENT_BIT_HELM_CHART_VERSION="0.1.32"
helm repo add --force-update eks https://aws.github.io/eks-charts/
tee "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-aws-for-fluent-bit.yml" << EOF
cloudWatchLogs:
region: ${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}
logGroupTemplate: "/aws/eks/${CLUSTER_NAME}/cluster"
logStreamTemplate: "\$kubernetes['namespace_name'].\$kubernetes['pod_name']"
serviceAccount:
create: false
name: aws-for-fluent-bit
serviceMonitor:
enabled: true
extraEndpoints:
- port: metrics
path: /metrics
interval: 30s
scrapeTimeout: 10s
scheme: http
EOF
helm upgrade --install --version "${AWS_FOR_FLUENT_BIT_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace aws-for-fluent-bit --values "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-aws-for-fluent-bit.yml" aws-for-fluent-bit eks/aws-for-fluent-bit
cert-manager
cert-manager adds certificates and certificate issuers as resource types in Kubernetes clusters and simplifies the process of obtaining, renewing, and using those certificates.
The cert-manager ServiceAccount was created by eksctl. Install the cert-manager Helm chart and modify its default values:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# renovate: datasource=helm depName=cert-manager registryUrl=https://charts.jetstack.io
CERT_MANAGER_HELM_CHART_VERSION="1.14.4"
helm repo add --force-update jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io
tee "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-cert-manager.yml" << EOF
installCRDs: true
serviceAccount:
create: false
name: cert-manager
extraArgs:
- --cluster-resource-namespace=cert-manager
- --enable-certificate-owner-ref=true
securityContext:
fsGroup: 1001
prometheus:
servicemonitor:
enabled: true
webhook:
networkPolicy:
enabled: true
EOF
helm upgrade --install --version "${CERT_MANAGER_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace cert-manager --create-namespace --wait --values "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-cert-manager.yml" cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager
kubectl label namespace cert-manager pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce=baseline
Add ClusterIssuers for the Let’s Encrypt staging environment:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
tee "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/k8s-cert-manager-clusterissuer-staging.yml" << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-staging-dns
namespace: cert-manager
labels:
letsencrypt: staging
spec:
acme:
server: https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
email: ${MY_EMAIL}
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-staging-dns
solvers:
- selector:
dnsZones:
- ${CLUSTER_FQDN}
dns01:
route53:
region: ${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}
EOF
kubectl wait --namespace cert-manager --timeout=15m --for=condition=Ready clusterissuer --all
Create the certificate:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
tee "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/k8s-cert-manager-certificate-staging.yml" << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: ingress-cert-staging
namespace: cert-manager
labels:
letsencrypt: staging
spec:
secretName: ingress-cert-staging
secretTemplate:
labels:
letsencrypt: staging
issuerRef:
name: letsencrypt-staging-dns
kind: ClusterIssuer
commonName: "*.${CLUSTER_FQDN}"
dnsNames:
- "*.${CLUSTER_FQDN}"
- "${CLUSTER_FQDN}"
EOF
external-dns
ExternalDNS synchronizes exposed Kubernetes Services and Ingresses with DNS providers.
ExternalDNS will manage the DNS records. The external-dns ServiceAccount was created by eksctl. Install the external-dns Helm chart and modify its default values:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# renovate: datasource=helm depName=external-dns registryUrl=https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/external-dns/
EXTERNAL_DNS_HELM_CHART_VERSION="1.14.3"
helm repo add --force-update external-dns https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/external-dns/
tee "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-external-dns.yml" << EOF
domainFilters:
- ${CLUSTER_FQDN}
interval: 20s
policy: sync
serviceAccount:
create: false
name: external-dns
serviceMonitor:
enabled: true
EOF
helm upgrade --install --version "${EXTERNAL_DNS_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace external-dns --values "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-external-dns.yml" external-dns external-dns/external-dns
kubectl label namespace external-dns pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce=baseline
ingress-nginx
ingress-nginx is an Ingress controller for Kubernetes that uses nginx as a reverse proxy and load balancer.
Install the ingress-nginx Helm chart and modify its default values:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
# renovate: datasource=helm depName=ingress-nginx registryUrl=https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
INGRESS_NGINX_HELM_CHART_VERSION="4.10.0"
kubectl wait --namespace cert-manager --for=condition=Ready --timeout=10m certificate ingress-cert-staging
helm repo add --force-update ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
tee "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-ingress-nginx.yml" << EOF
controller:
allowSnippetAnnotations: true
ingressClassResource:
default: true
admissionWebhooks:
networkPolicyEnabled: true
extraArgs:
default-ssl-certificate: "cert-manager/ingress-cert-staging"
service:
annotations:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-type: nlb
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-additional-resource-tags: ${TAGS//\'/}
metrics:
enabled: true
serviceMonitor:
enabled: true
prometheusRule:
enabled: true
rules:
- alert: NGINXConfigFailed
expr: count(nginx_ingress_controller_config_last_reload_successful == 0) > 0
for: 1s
labels:
severity: critical
annotations:
description: bad ingress config - nginx config test failed
summary: uninstall the latest ingress changes to allow config reloads to resume
- alert: NGINXCertificateExpiry
expr: (avg(nginx_ingress_controller_ssl_expire_time_seconds) by (host) - time()) < 604800
for: 1s
labels:
severity: critical
annotations:
description: ssl certificate(s) will expire in less then a week
summary: renew expiring certificates to avoid downtime
- alert: NGINXTooMany500s
expr: 100 * ( sum( nginx_ingress_controller_requests{status=~"5.+"} ) / sum(nginx_ingress_controller_requests) ) > 5
for: 1m
labels:
severity: warning
annotations:
description: Too many 5XXs
summary: More than 5% of all requests returned 5XX, this requires your attention
- alert: NGINXTooMany400s
expr: 100 * ( sum( nginx_ingress_controller_requests{status=~"4.+"} ) / sum(nginx_ingress_controller_requests) ) > 5
for: 1m
labels:
severity: warning
annotations:
description: Too many 4XXs
summary: More than 5% of all requests returned 4XX, this requires your attention
EOF
helm upgrade --install --version "${INGRESS_NGINX_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace ingress-nginx --create-namespace --wait --values "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-ingress-nginx.yml" ingress-nginx ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx
kubectl label namespace ingress-nginx pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce=baseline
forecastle
Forecastle is a control panel that dynamically discovers and provides a launchpad for accessing applications deployed on Kubernetes.
Install the forecastle Helm chart and modify its default values:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# renovate: datasource=helm depName=forecastle registryUrl=https://stakater.github.io/stakater-charts
FORECASTLE_HELM_CHART_VERSION="1.0.138"
helm repo add --force-update stakater https://stakater.github.io/stakater-charts
tee "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-forecastle.yml" << EOF
forecastle:
config:
namespaceSelector:
any: true
title: Launch Pad
networkPolicy:
enabled: true
ingress:
enabled: true
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-signin: https://oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_FQDN}/oauth2/start?rd=\$scheme://\$host\$request_uri
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-url: https://oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_FQDN}/oauth2/auth
className: nginx
hosts:
- host: ${CLUSTER_FQDN}
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
tls:
- hosts:
- ${CLUSTER_FQDN}
EOF
helm upgrade --install --version "${FORECASTLE_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace forecastle --create-namespace --values "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-forecastle.yml" forecastle stakater/forecastle
kubectl label namespace forecastle pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce=baseline
oauth2-proxy
Use OAuth2 Proxy to protect application endpoints with Google Authentication.
Install the oauth2-proxy Helm chart and modify its default values:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
# renovate: datasource=helm depName=oauth2-proxy registryUrl=https://oauth2-proxy.github.io/manifests
OAUTH2_PROXY_HELM_CHART_VERSION="6.24.2"
set +x
COOKIE_SECRET="$(openssl rand -base64 32 | head -c 32 | base64)"
echo "::add-mask::${COOKIE_SECRET}"
set -x
helm repo add --force-update oauth2-proxy https://oauth2-proxy.github.io/manifests
tee "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-oauth2-proxy.yml" << EOF
config:
clientID: ${GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID}
clientSecret: ${GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET}
cookieSecret: ${COOKIE_SECRET}
configFile: |-
cookie_domains = ".${CLUSTER_FQDN}"
set_authorization_header = "true"
set_xauthrequest = "true"
upstreams = [ "file:///dev/null" ]
whitelist_domains = ".${CLUSTER_FQDN}"
authenticatedEmailsFile:
enabled: true
restricted_access: |-
${MY_EMAIL}
ingress:
enabled: true
className: nginx
hosts:
- oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_FQDN}
tls:
- hosts:
- oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_FQDN}
metrics:
servicemonitor:
enabled: true
EOF
helm upgrade --install --version "${OAUTH2_PROXY_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace oauth2-proxy --create-namespace --values "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/helm_values-oauth2-proxy.yml" oauth2-proxy oauth2-proxy/oauth2-proxy
kubectl label namespace oauth2-proxy pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce=baseline
Enforce Pod Security Standards with Namespace Labels
Label all namespaces to provide warnings when configurations deviate from Pod Security Standards:
1
kubectl label namespace --all pod-security.kubernetes.io/warn=baseline
Details can be found in: Enforce Pod Security Standards with Namespace Labels
Clean-up
Remove the EKS cluster and its created components:
1
2
3
if eksctl get cluster --name="${CLUSTER_NAME}"; then
eksctl delete cluster --name="${CLUSTER_NAME}" --force
fi
Remove the Route 53 DNS records from the DNS Zone:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
CLUSTER_FQDN_ZONE_ID=$(aws route53 list-hosted-zones --query "HostedZones[?Name==\`${CLUSTER_FQDN}.\`].Id" --output text)
if [[ -n "${CLUSTER_FQDN_ZONE_ID}" ]]; then
aws route53 list-resource-record-sets --hosted-zone-id "${CLUSTER_FQDN_ZONE_ID}" | jq -c '.ResourceRecordSets[] | select (.Type != "SOA" and .Type != "NS")' |
while read -r RESOURCERECORDSET; do
aws route53 change-resource-record-sets \
--hosted-zone-id "${CLUSTER_FQDN_ZONE_ID}" \
--change-batch '{"Changes":[{"Action":"DELETE","ResourceRecordSet": '"${RESOURCERECORDSET}"' }]}' \
--output text --query 'ChangeInfo.Id'
done
fi
Remove any orphan EC2 instances created by Karpenter:
1
2
3
4
for EC2 in $(aws ec2 describe-instances --filters "Name=tag:kubernetes.io/cluster/${CLUSTER_NAME},Values=owned" Name=instance-state-name,Values=running --query "Reservations[].Instances[].InstanceId" --output text); do
echo "Removing EC2: ${EC2}"
aws ec2 terminate-instances --instance-ids "${EC2}"
done
Remove the CloudWatch log group:
1
2
3
if [[ "$(aws logs describe-log-groups --query "logGroups[?logGroupName==\`/aws/eks/${CLUSTER_NAME}/cluster\`] | [0].logGroupName" --output text)" = "/aws/eks/${CLUSTER_NAME}/cluster" ]]; then
aws logs delete-log-group --log-group-name "/aws/eks/${CLUSTER_NAME}/cluster"
fi
Remove the CloudFormation stack:
1
aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name "${CLUSTER_NAME}-route53-kms"
Wait for all CloudFormation stacks to complete deletion:
1
2
aws cloudformation wait stack-delete-complete --stack-name "${CLUSTER_NAME}-route53-kms"
aws cloudformation wait stack-delete-complete --stack-name "eksctl-${CLUSTER_NAME}-cluster"
Remove volumes and snapshots related to the cluster (as a precaution):
1
2
3
4
for VOLUME in $(aws ec2 describe-volumes --filter "Name=tag:KubernetesCluster,Values=${CLUSTER_NAME}" "Name=tag:kubernetes.io/cluster/${CLUSTER_NAME},Values=owned" --query 'Volumes[].VolumeId' --output text); do
echo "*** Removing Volume: ${VOLUME}"
aws ec2 delete-volume --volume-id "${VOLUME}"
done
Remove the ${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN} directory:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
if [[ -d "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}" ]]; then
for FILE in "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}"/{kubeconfig-${CLUSTER_NAME}.conf,{aws-cf-route53-kms,eksctl-${CLUSTER_NAME},k8s-karpenter-provisioner,helm_values-{aws-ebs-csi-driver,aws-for-fluent-bit,cert-manager,external-dns,forecastle,ingress-nginx,karpenter,kube-prometheus-stack,mailpit,oauth2-proxy},k8s-cert-manager-{certificate,clusterissuer}-staging}.yml}; do
if [[ -f "${FILE}" ]]; then
rm -v "${FILE}"
else
echo "*** File not found: ${FILE}"
fi
done
rmdir "${TMP_DIR}/${CLUSTER_FQDN}"
fi
Enjoy … 😉