# Nginx + cert-manager + kubed installation
Before we move on with other tasks it is necessary to install Nginx Ingress. It's also handy to install cert-manager for managing SSL certificates.
# Install cert-manager
cert-manager architecture:
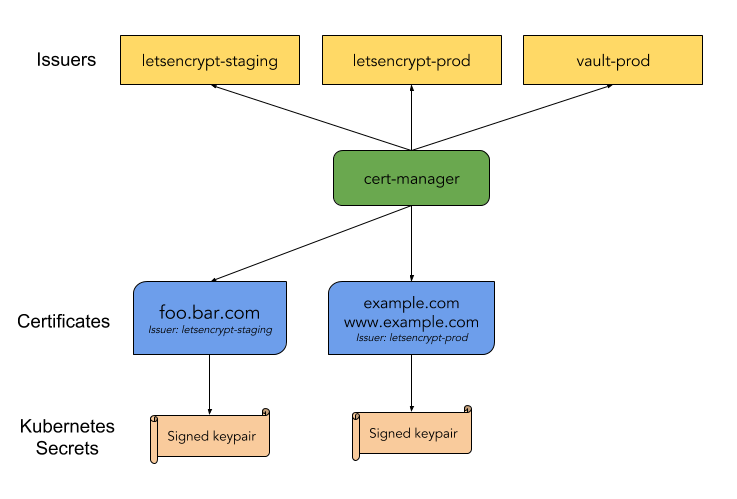
Install the CRDs resources separately:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jetstack/cert-manager/release-0.10/deploy/manifests/00-crds.yaml
Output:
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/certificates.certmanager.k8s.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/challenges.certmanager.k8s.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/clusterissuers.certmanager.k8s.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/issuers.certmanager.k8s.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/orders.certmanager.k8s.io created
Create the namespace for cert-manager and label it to disable resource validation:
kubectl create namespace cert-manager
kubectl label namespace cert-manager certmanager.k8s.io/disable-validation=true
Output:
namespace/cert-manager created
namespace/cert-manager labeled
Install the cert-manager Helm chart:
helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io
helm install --name cert-manager --namespace cert-manager --wait jetstack/cert-manager --version v0.10.0
Output:
"jetstack" has been added to your repositories
NAME: cert-manager
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Jul 19 11:47:58 2019
NAMESPACE: cert-manager
STATUS: DEPLOYED
RESOURCES:
==> v1/ClusterRole
NAME AGE
cert-manager-edit 10s
cert-manager-view 10s
==> v1/Pod(related)
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cert-manager-578fc6ff6-qjvrr 1/1 Running 0 10s
cert-manager-cainjector-5975fd64c5-82c8x 1/1 Running 0 10s
==> v1/ServiceAccount
NAME SECRETS AGE
cert-manager 1 10s
cert-manager-cainjector 1 10s
==> v1beta1/ClusterRole
NAME AGE
cert-manager 10s
cert-manager-cainjector 10s
==> v1beta1/ClusterRoleBinding
NAME AGE
cert-manager 10s
cert-manager-cainjector 10s
==> v1beta1/Deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
cert-manager 1/1 1 1 10s
cert-manager-cainjector 1/1 1 1 10s
NOTES:
cert-manager has been deployed successfully!
In order to begin issuing certificates, you will need to set up a ClusterIssuer
or Issuer resource (for example, by creating a 'letsencrypt-staging' issuer).
More information on the different types of issuers and how to configure them
can be found in our documentation:
https://docs.cert-manager.io/en/latest/reference/issuers.html
For information on how to configure cert-manager to automatically provision
Certificates for Ingress resources, take a look at the `ingress-shim`
documentation:
https://docs.cert-manager.io/en/latest/reference/ingress-shim.html
# Create ClusterIssuer for Let's Encrypt
Create ClusterIssuer for Route53 used by cert-manager. It will allow Let's
Encrypt to generate certificate. Route53 (DNS) method of requesting certificate
from Let's Encrypt must be used to create wildcard certificate *.mylabs.dev
(details here (opens new window)).

(https://b3n.org/intranet-ssl-certificates-using-lets-encrypt-dns-01/ (opens new window))
export EKS_CERT_MANAGER_ROUTE53_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY_BASE64=$(echo -n "$EKS_CERT_MANAGER_ROUTE53_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY" | base64)
envsubst < files/cert-manager-letsencrypt-aws-route53-clusterissuer.yaml | kubectl apply -f -
cat files/cert-manager-letsencrypt-aws-route53-clusterissuer.yaml
Output:
secret/aws-route53-secret-access-key-secret created
clusterissuer.certmanager.k8s.io/selfsigning-issuer created
clusterissuer.certmanager.k8s.io/letsencrypt-staging-dns created
clusterissuer.certmanager.k8s.io/letsencrypt-production-dns created
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: aws-route53-secret-access-key-secret
namespace: cert-manager
data:
secret-access-key: $EKS_CERT_MANAGER_ROUTE53_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY_BASE64
---
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: selfsigning-issuer
spec:
selfSigned: {}
---
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-staging-dns
namespace: cert-manager
spec:
acme:
# The ACME server URL
server: https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
# Email address used for ACME registration
email: petr.ruzicka@gmail.com
# Name of a secret used to store the ACME account private key
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-staging-dns
dns01:
# Here we define a list of DNS-01 providers that can solve DNS challenges
providers:
- name: aws-route53
route53:
accessKeyID: ${EKS_CERT_MANAGER_ROUTE53_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID}
region: eu-central-1
secretAccessKeySecretRef:
name: aws-route53-secret-access-key-secret
key: secret-access-key
---
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-production-dns
namespace: cert-manager
spec:
acme:
# The ACME server URL
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
# Email address used for ACME registration
email: petr.ruzicka@gmail.com
# Name of a secret used to store the ACME account private key
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-production-dns
dns01:
# Here we define a list of DNS-01 providers that can solve DNS challenges
providers:
- name: aws-route53
route53:
accessKeyID: ${EKS_CERT_MANAGER_ROUTE53_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID}
region: eu-central-1
secretAccessKeySecretRef:
name: aws-route53-secret-access-key-secret
key: secret-access-key
# Generate TLS certificate
Create certificate using cert-manager:
envsubst < files/cert-manager-letsencrypt-aws-route53-certificate.yaml | kubectl apply -f -
envsubst < files/cert-manager-letsencrypt-aws-route53-certificate.yaml
Output:
certificate.certmanager.k8s.io/ingress-cert-production created
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: ingress-cert-production
namespace: cert-manager
spec:
secretName: ingress-cert-production
issuerRef:
kind: ClusterIssuer
name: letsencrypt-production-dns
commonName: "*.mylabs.dev"
dnsNames:
- "*.mylabs.dev"
acme:
config:
- dns01:
provider: aws-route53
domains:
- "*.mylabs.dev"
# Install kubed
It's necessary to copy the wildcard certificate across all "future" namespaces and that's the reason why kubed (opens new window) needs to be installed (for now). kubed (opens new window) can synchronize ConfigMaps/Secrets (opens new window) across Kubernetes namespaces/clusters.
Kubed - synchronize secret diagram:
Add kubed helm repository:
helm repo add appscode https://charts.appscode.com/stable/
Output:
"appscode" has been added to your repositories
Install kubed:
helm install appscode/kubed --name kubed --version 0.11.0 --namespace kube-system --wait \
--set config.clusterName=my_k8s_cluster \
--set apiserver.enabled=false
Output:
NAME: kubed
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Jul 19 11:48:10 2019
NAMESPACE: kube-system
STATUS: DEPLOYED
RESOURCES:
==> v1/ClusterRole
NAME AGE
kubed-kubed 4s
==> v1/ClusterRoleBinding
NAME AGE
kubed-kubed 4s
kubed-kubed-apiserver-auth-delegator 4s
==> v1/Pod(related)
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kubed-kubed-75789b6cc6-6zrst 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 4s
==> v1/RoleBinding
NAME AGE
kubed-kubed-apiserver-extension-server-authentication-reader 4s
==> v1/Secret
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
kubed-kubed Opaque 1 4s
kubed-kubed-apiserver-cert Opaque 2 4s
==> v1/Service
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubed-kubed ClusterIP 10.100.193.123 <none> 443/TCP 4s
==> v1/ServiceAccount
NAME SECRETS AGE
kubed-kubed 1 4s
==> v1beta1/Deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
kubed-kubed 0/1 1 0 4s
NOTES:
To verify that Kubed has started, run:
kubectl --namespace=kube-system get deployments -l "release=kubed, app=kubed"
Annotate (mark) the cert-manager secret to be copied to other namespaces if necessary:
kubectl annotate secret ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT} -n cert-manager kubed.appscode.com/sync="app=kubed"
Output:
secret/ingress-cert-production annotated
# Install nginx-ingress
(https://www.nginx.com/blog/ (opens new window))
Install nginx-ingress which will also create a new loadbalancer:
helm install stable/nginx-ingress --wait --name nginx-ingress --namespace nginx-ingress-system --version 1.24.3 \
--set rbac.create=true \
--set controller.extraArgs.default-ssl-certificate=cert-manager/ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT}
Output:
NAME: nginx-ingress
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Jul 19 11:48:17 2019
NAMESPACE: nginx-ingress-system
STATUS: DEPLOYED
RESOURCES:
==> v1/ConfigMap
NAME DATA AGE
nginx-ingress-controller 1 8s
==> v1/Pod(related)
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-ingress-controller-7b59c7c7bc-nhmq8 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 8s
nginx-ingress-default-backend-6d489448cb-d9brb 1/1 Running 0 8s
==> v1/Service
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx-ingress-controller LoadBalancer 10.100.37.102 a55fd2fadaa0a... 80:30958/TCP,443:31932/TCP 8s
nginx-ingress-default-backend ClusterIP 10.100.15.87 <none> 80/TCP 8s
==> v1/ServiceAccount
NAME SECRETS AGE
nginx-ingress 1 8s
==> v1beta1/ClusterRole
NAME AGE
nginx-ingress 8s
==> v1beta1/ClusterRoleBinding
NAME AGE
nginx-ingress 8s
==> v1beta1/Deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx-ingress-controller 0/1 1 0 8s
nginx-ingress-default-backend 1/1 1 1 8s
==> v1beta1/Role
NAME AGE
nginx-ingress 8s
==> v1beta1/RoleBinding
NAME AGE
nginx-ingress 8s
NOTES:
The nginx-ingress controller has been installed.
It may take a few minutes for the LoadBalancer IP to be available.
You can watch the status by running 'kubectl --namespace nginx-ingress-system get services -o wide -w nginx-ingress-controller'
An example Ingress that makes use of the controller:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
name: example
namespace: foo
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: exampleService
servicePort: 80
path: /
# This section is only required if TLS is to be enabled for the Ingress
tls:
- hosts:
- www.example.com
secretName: example-tls
If TLS is enabled for the Ingress, a Secret containing the certificate and key must also be provided:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: example-tls
namespace: foo
data:
tls.crt: <base64 encoded cert>
tls.key: <base64 encoded key>
type: kubernetes.io/tls
# Create DNS records
nginx-ingress created the loadbalancer service. In case of AWS it is Classic Elastic Loadbalancer:
kubectl get service -n nginx-ingress-system
Output:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx-ingress-controller LoadBalancer 10.100.37.102 a55fd2fadaa0a11e9bcf2026dca96845-1478956562.eu-central-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:30958/TCP,443:31932/TCP 8s
nginx-ingress-default-backend ClusterIP 10.100.15.87 <none> 80/TCP 8s
Create DNS record mylabs.dev for the loadbalancer created by nginx-ingress:
export LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME=$(kubectl get svc nginx-ingress-controller -n nginx-ingress-system -o jsonpath="{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].hostname}")
export CANONICAL_HOSTED_ZONE_NAME_ID=$(aws elb describe-load-balancers --query "LoadBalancerDescriptions[?DNSName==\`$LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME\`].CanonicalHostedZoneNameID" --output text)
export HOSTED_ZONE_ID=$(aws route53 list-hosted-zones --query "HostedZones[?Name==\`${MY_DOMAIN}.\`].Id" --output text)
envsubst < files/aws_route53-dns_change.json | aws route53 change-resource-record-sets --hosted-zone-id ${HOSTED_ZONE_ID} --change-batch=file:///dev/stdin | jq
Output:
{
"ChangeInfo": {
"Id": "/change/C2YV79SSX0CS95",
"Status": "PENDING",
"SubmittedAt": "2019-07-19T09:48:29.092Z",
"Comment": "A new record set for the zone."
}
}
Wait for completion of certificate create process:
COUNT=0; OUTPUT=""; while [ "${OUTPUT}" != "True" ] && [ "${COUNT}" -lt 100 ]; do COUNT=$((COUNT+1)); OUTPUT=$(kubectl get certificate ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT} -n cert-manager -o jsonpath="{.status.conditions[0].status}"); sleep 1; echo -n "${COUNT} "; done
You should see the following output form cert-manager when looking at certificates:
kubectl describe certificates -n cert-manager ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT}
Output
Name: ingress-cert-production
Namespace: cert-manager
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1","kind":"Certificate","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"ingress-cert-production","namespace"...
API Version: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
Kind: Certificate
Metadata:
Creation Timestamp: 2019-07-19T09:48:10Z
Generation: 4
Resource Version: 2919
Self Link: /apis/certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1/namespaces/cert-manager/certificates/ingress-cert-production
UID: 5131721b-aa0a-11e9-bcf2-026dca968456
Spec:
Acme:
Config:
Dns 01:
Provider: aws-route53
Domains:
*.mylabs.dev
Common Name: *.mylabs.dev
Dns Names:
*.mylabs.dev
Issuer Ref:
Kind: ClusterIssuer
Name: letsencrypt-production-dns
Secret Name: ingress-cert-production
Status:
Conditions:
Last Transition Time: 2019-07-19T09:49:54Z
Message: Certificate is up to date and has not expired
Reason: Ready
Status: True
Type: Ready
Not After: 2019-10-17T08:49:53Z
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Warning IssuerNotReady 105s (x2 over 105s) cert-manager Issuer letsencrypt-production-dns not ready
Normal Generated 105s cert-manager Generated new private key
Normal GenerateSelfSigned 105s cert-manager Generated temporary self signed certificate
Normal OrderCreated 105s cert-manager Created Order resource "ingress-cert-production-20059064"
Normal OrderComplete 1s cert-manager Order "ingress-cert-production-20059064" completed successfully
Normal CertIssued 1s cert-manager Certificate issued successfully
The Kubernetes "secret" in cert-manager namespace should contain the
certificates:
kubectl describe secret -n cert-manager ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT}
Output:
Name: ingress-cert-production
Namespace: cert-manager
Labels: certmanager.k8s.io/certificate-name=ingress-cert-production
Annotations: certmanager.k8s.io/alt-names: *.mylabs.dev
certmanager.k8s.io/common-name: *.mylabs.dev
certmanager.k8s.io/ip-sans:
certmanager.k8s.io/issuer-kind: ClusterIssuer
certmanager.k8s.io/issuer-name: letsencrypt-production-dns
kubed.appscode.com/sync: app=kubed
Type: kubernetes.io/tls
Data
====
ca.crt: 0 bytes
tls.crt: 3550 bytes
tls.key: 1675 bytes
Check the SSL certificate:
while ! echo | openssl s_client -showcerts -connect ${MY_DOMAIN}:443 &> /dev/null; do sleep 1; echo -n ". "; done
echo | openssl s_client -showcerts -connect ${MY_DOMAIN}:443 | openssl x509 -inform pem -noout -text
Output:
depth=2 O = Digital Signature Trust Co., CN = DST Root CA X3
verify return:1
depth=1 C = US, O = Let's Encrypt, CN = Let's Encrypt Authority X3
verify return:1
depth=0 CN = *.mylabs.dev
verify return:1
DONE
Certificate:
Data:
Version: 3 (0x2)
Serial Number:
03:cf:14:18:90:0e:c8:7f:c2:39:eb:e5:dc:42:d7:c6:7a:a6
Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
Issuer: C = US, O = Let's Encrypt, CN = Let's Encrypt Authority X3
Validity
Not Before: Jul 19 08:49:53 2019 GMT
Not After : Oct 17 08:49:53 2019 GMT
Subject: CN = *.mylabs.dev
Subject Public Key Info:
Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption
RSA Public-Key: (2048 bit)
Modulus:
...
Exponent: 65537 (0x10001)
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Key Usage: critical
Digital Signature, Key Encipherment
X509v3 Extended Key Usage:
TLS Web Server Authentication, TLS Web Client Authentication
X509v3 Basic Constraints: critical
CA:FALSE
X509v3 Subject Key Identifier:
44:C9:D2:B1:71:D6:94:92:67:DB:8C:C9:7E:0C:68:10:C3:10:41:D9
X509v3 Authority Key Identifier:
keyid:A8:4A:6A:63:04:7D:DD:BA:E6:D1:39:B7:A6:45:65:EF:F3:A8:EC:A1
Authority Information Access:
OCSP - URI:http://ocsp.int-x3.letsencrypt.org
CA Issuers - URI:http://cert.int-x3.letsencrypt.org/
X509v3 Subject Alternative Name:
DNS:*.mylabs.dev
X509v3 Certificate Policies:
Policy: 2.23.140.1.2.1
Policy: 1.3.6.1.4.1.44947.1.1.1
CPS: http://cps.letsencrypt.org
...

