Amazon EKS with Rancher
- GitHub repository: https://github.com/ruzickap/k8s-eks-rancher
- Web Pages: https://ruzickap.github.io/k8s-eks-rancher
Requirements
- awscli
- AWS account
- Helm
- kubectl
- eksctl
- Kubernetes and AWS knowledge required
Prepare AWS Account
- Requirements
- Prepare the local working environment
- Configure AWS Route 53 Domain delegation
- Allow GH Actions to connect to AWS accounts
Requirements
If you would like to follow this documents and it's task you will need to set up few environment variables.
BASE_DOMAIN (k8s.mylabs.dev) contains DNS records for all your Kubernetes
clusters. The cluster names will look like CLUSTER_NAME.BASE_DOMAIN
(kube1.k8s.mylabs.dev).
# AWS Region
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION="${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION:-eu-central-1}"
# Hostname / FQDN definitions
export CLUSTER_FQDN="${CLUSTER_FQDN:-mgmt1.k8s.use1.dev.proj.aws.mylabs.dev}"
export BASE_DOMAIN="${CLUSTER_FQDN#*.}"
export CLUSTER_NAME="${CLUSTER_FQDN%%.*}"
export KUBECONFIG="${PWD}/tmp/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/kubeconfig-${CLUSTER_NAME}.conf"
export LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT="staging"
export MY_EMAIL="petr.ruzicka@gmail.com"
# Tags used to tag the AWS resources
export TAGS="Owner=${MY_EMAIL} Environment=dev Group=Cloud_Native Squad=Cloud_Container_Platform"
You will need to configure AWS CLI and other secrets/variables.
# AWS Credentials
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="******************"
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="******************"
# Rancher password
export MY_PASSWORD="**********"
# export AWS_SESSION_TOKEN="**********"
Verify if all the necessary variables were set:
: "${AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID?}"
: "${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION?}"
: "${AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY?}"
: "${BASE_DOMAIN?}"
: "${CLUSTER_FQDN?}"
: "${CLUSTER_NAME?}"
: "${KUBECONFIG?}"
: "${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT?}"
: "${MY_EMAIL?}"
: "${MY_PASSWORD}"
: "${TAGS?}"
echo -e "${MY_EMAIL} | ${CLUSTER_NAME} | ${BASE_DOMAIN} | ${CLUSTER_FQDN}\n${TAGS}"
Prepare the local working environment
Install necessary software:
if command -v apt-get &> /dev/null; then
apt update -qq
apt-get install -y -qq curl git jq sudo unzip > /dev/null
fi
Install AWS CLI binary:
if ! command -v aws &> /dev/null; then
# renovate: datasource=github-tags depName=aws/aws-cli
AWSCLI_VERSION="2.17.6"
curl -sL "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64-${AWSCLI_VERSION}.zip" -o "/tmp/awscli.zip"
unzip -q -o /tmp/awscli.zip -d /tmp/
sudo /tmp/aws/install
fi
Install eksctl:
if ! command -v eksctl &> /dev/null; then
# renovate: datasource=github-tags depName=weaveworks/eksctl
EKSCTL_VERSION="0.183.0"
curl -s -L "https://github.com/weaveworks/eksctl/releases/download/v${EKSCTL_VERSION}/eksctl_$(uname)_amd64.tar.gz" | sudo tar xz -C /usr/local/bin/
fi
Install kubectl binary:
if ! command -v kubectl &> /dev/null; then
# renovate: datasource=github-tags depName=kubernetes/kubectl extractVersion=^kubernetes-(?<version>.+)$
KUBECTL_VERSION="1.30.2"
sudo curl -s -Lo /usr/local/bin/kubectl "https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v${KUBECTL_VERSION}/bin/$(uname | sed "s/./\L&/g")/amd64/kubectl"
sudo chmod a+x /usr/local/bin/kubectl
fi
Install Helm:
if ! command -v helm &> /dev/null; then
# renovate: datasource=github-tags depName=helm/helm
HELM_VERSION="3.15.2"
curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/master/scripts/get | bash -s -- --version "v${HELM_VERSION}"
fi
Configure AWS Route 53 Domain delegation
DNS delegation should be done only once.
Create DNS zone for EKS clusters:
export CLOUDFLARE_EMAIL="petr.ruzicka@gmail.com"
export CLOUDFLARE_API_KEY="11234567890"
aws route53 create-hosted-zone --output json \
--name "${BASE_DOMAIN}" \
--caller-reference "$(date)" \
--hosted-zone-config="{\"Comment\": \"Created by petr.ruzicka@gmail.com\", \"PrivateZone\": false}" | jq
Use your domain registrar to change the nameservers for your zone (for example
mylabs.dev) to use the Amazon Route 53 nameservers. Here is the way how you
can find out the the Route 53 nameservers:
NEW_ZONE_ID=$(aws route53 list-hosted-zones --query "HostedZones[?Name==\`${BASE_DOMAIN}.\`].Id" --output text)
NEW_ZONE_NS=$(aws route53 get-hosted-zone --output json --id "${NEW_ZONE_ID}" --query "DelegationSet.NameServers")
NEW_ZONE_NS1=$(echo "${NEW_ZONE_NS}" | jq -r ".[0]")
NEW_ZONE_NS2=$(echo "${NEW_ZONE_NS}" | jq -r ".[1]")
Create the NS record in k8s.use1.dev.proj.aws.mylabs.dev (BASE_DOMAIN) for
proper zone delegation. This step depends on your domain registrar - I'm using
CloudFlare and using Ansible to automate it:
ansible -m cloudflare_dns -c local -i "localhost," localhost -a "zone=mylabs.dev record=${BASE_DOMAIN} type=NS value=${NEW_ZONE_NS1} solo=true proxied=no account_email=${CLOUDFLARE_EMAIL} account_api_token=${CLOUDFLARE_API_KEY}"
ansible -m cloudflare_dns -c local -i "localhost," localhost -a "zone=mylabs.dev record=${BASE_DOMAIN} type=NS value=${NEW_ZONE_NS2} solo=false proxied=no account_email=${CLOUDFLARE_EMAIL} account_api_token=${CLOUDFLARE_API_KEY}"
Output:
localhost | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"result": {
"record": {
"content": "ns-885.awsdns-46.net",
"created_on": "2020-11-13T06:25:32.18642Z",
"id": "dxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxb",
"locked": false,
"meta": {
"auto_added": false,
"managed_by_apps": false,
"managed_by_argo_tunnel": false,
"source": "primary"
},
"modified_on": "2020-11-13T06:25:32.18642Z",
"name": "k8s.mylabs.dev",
"proxiable": false,
"proxied": false,
"ttl": 1,
"type": "NS",
"zone_id": "2xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxe",
"zone_name": "mylabs.dev"
}
}
}
localhost | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"result": {
"record": {
"content": "ns-1692.awsdns-19.co.uk",
"created_on": "2020-11-13T06:25:37.605605Z",
"id": "9xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxb",
"locked": false,
"meta": {
"auto_added": false,
"managed_by_apps": false,
"managed_by_argo_tunnel": false,
"source": "primary"
},
"modified_on": "2020-11-13T06:25:37.605605Z",
"name": "k8s.mylabs.dev",
"proxiable": false,
"proxied": false,
"ttl": 1,
"type": "NS",
"zone_id": "2xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxe",
"zone_name": "mylabs.dev"
}
}
}
Allow GH Actions to connect to AWS accounts
You also need to allow GitHub Action to connect to the AWS account(s) where you want to provision the clusters.
Example: AWS federation comes to GitHub Actions
aws cloudformation deploy --region=eu-central-1 --capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--parameter-overrides "GitHubFullRepositoryName=ruzickap/k8s-eks-rancher" \
--stack-name "${USER}-k8s-eks-rancher-gh-action-iam-role-oidc" \
--template-file "./cloudformation/gh-action-iam-role-oidc.yaml" \
--tags "Owner=petr.ruzicka@gmail.com"
Create additional AWS structure and Amazon EKS
Create Route53
Create CloudFormation template containing policies for Route53 and Domain.
Put new domain CLUSTER_FQDN to the Route 53 and configure the DNS delegation
from the BASE_DOMAIN.
Create temporary directory for files used for creating/configuring EKS Cluster and it's components:
mkdir -p "tmp/${CLUSTER_FQDN}"
Create Route53 zone:
cat > "tmp/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/cf-route53.yml" << \EOF
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: Route53 entries
Parameters:
BaseDomain:
Description: "Base domain where cluster domains + their subdomains will live. Ex: k8s.mylabs.dev"
Type: String
ClusterFQDN:
Description: "Cluster FQDN. (domain for all applications) Ex: kube1.k8s.mylabs.dev"
Type: String
Resources:
HostedZone:
Type: AWS::Route53::HostedZone
Properties:
Name: !Ref ClusterFQDN
RecordSet:
Type: AWS::Route53::RecordSet
Properties:
HostedZoneName: !Sub "${BaseDomain}."
Name: !Ref ClusterFQDN
Type: NS
TTL: 60
ResourceRecords: !GetAtt HostedZone.NameServers
EOF
if [[ $(aws cloudformation list-stacks --stack-status-filter CREATE_COMPLETE --query "StackSummaries[?starts_with(StackName, \`${CLUSTER_NAME}-route53\`) == \`true\`].StackName" --output text) == "" ]]; then
# shellcheck disable=SC2001
eval aws cloudformation "create-stack" \
--parameters "ParameterKey=BaseDomain,ParameterValue=${BASE_DOMAIN} ParameterKey=ClusterFQDN,ParameterValue=${CLUSTER_FQDN}" \
--stack-name "${CLUSTER_NAME}-route53" \
--template-body "file://tmp/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/cf-route53.yml" \
--tags "$(echo "${TAGS}" | sed -e 's/\([^ =]*\)=\([^ ]*\)/Key=\1,Value=\2/g')" || true
fi
Create Amazon EKS
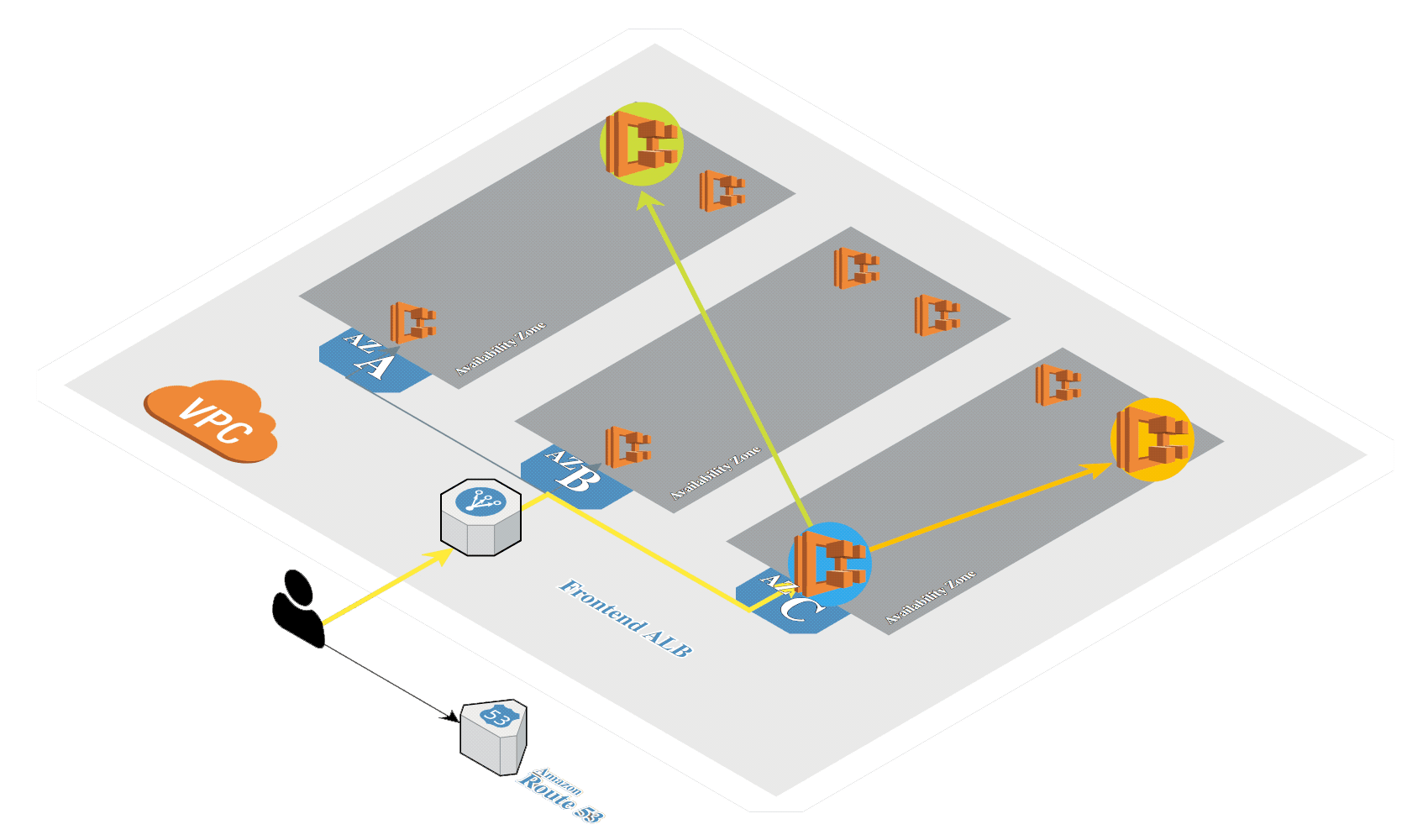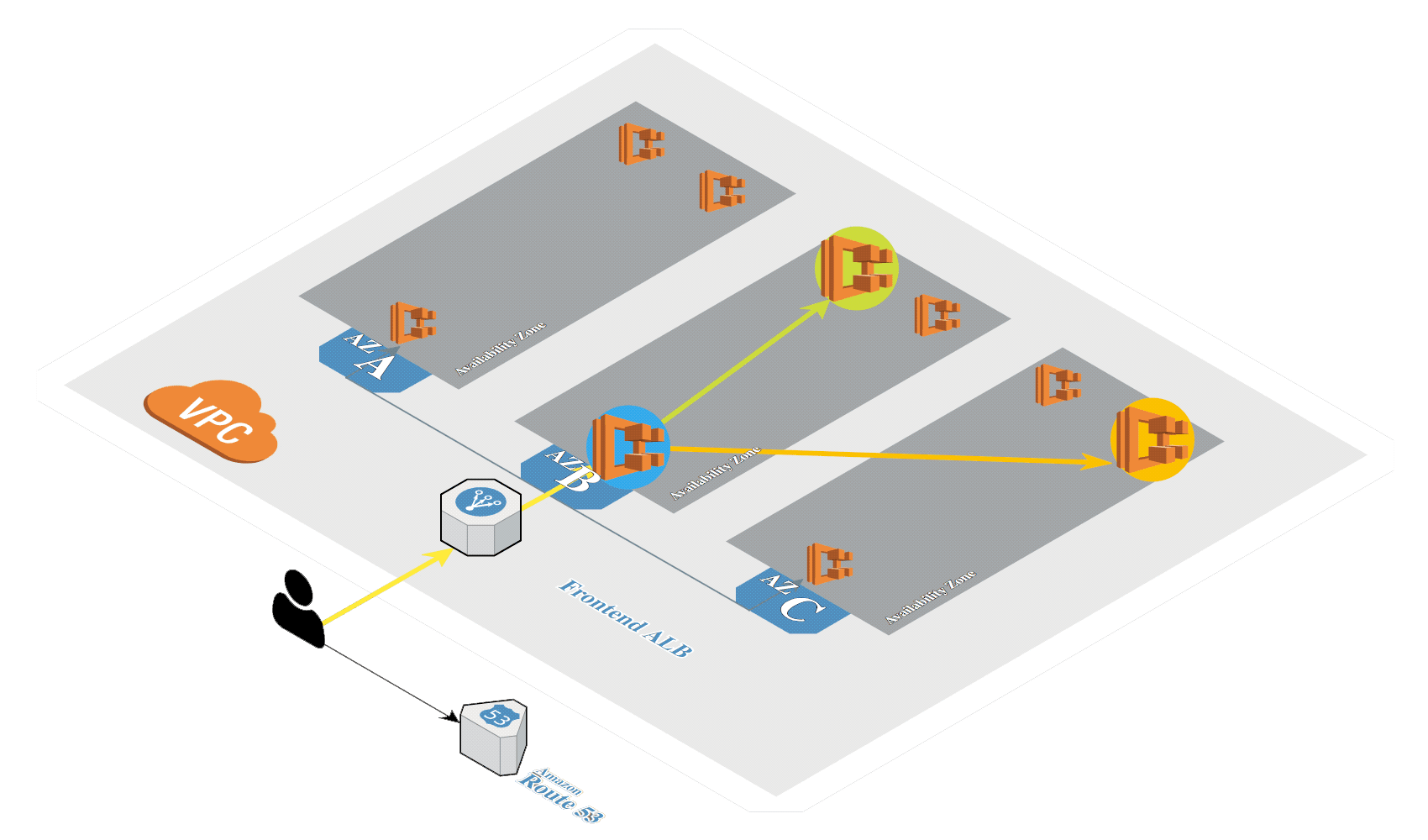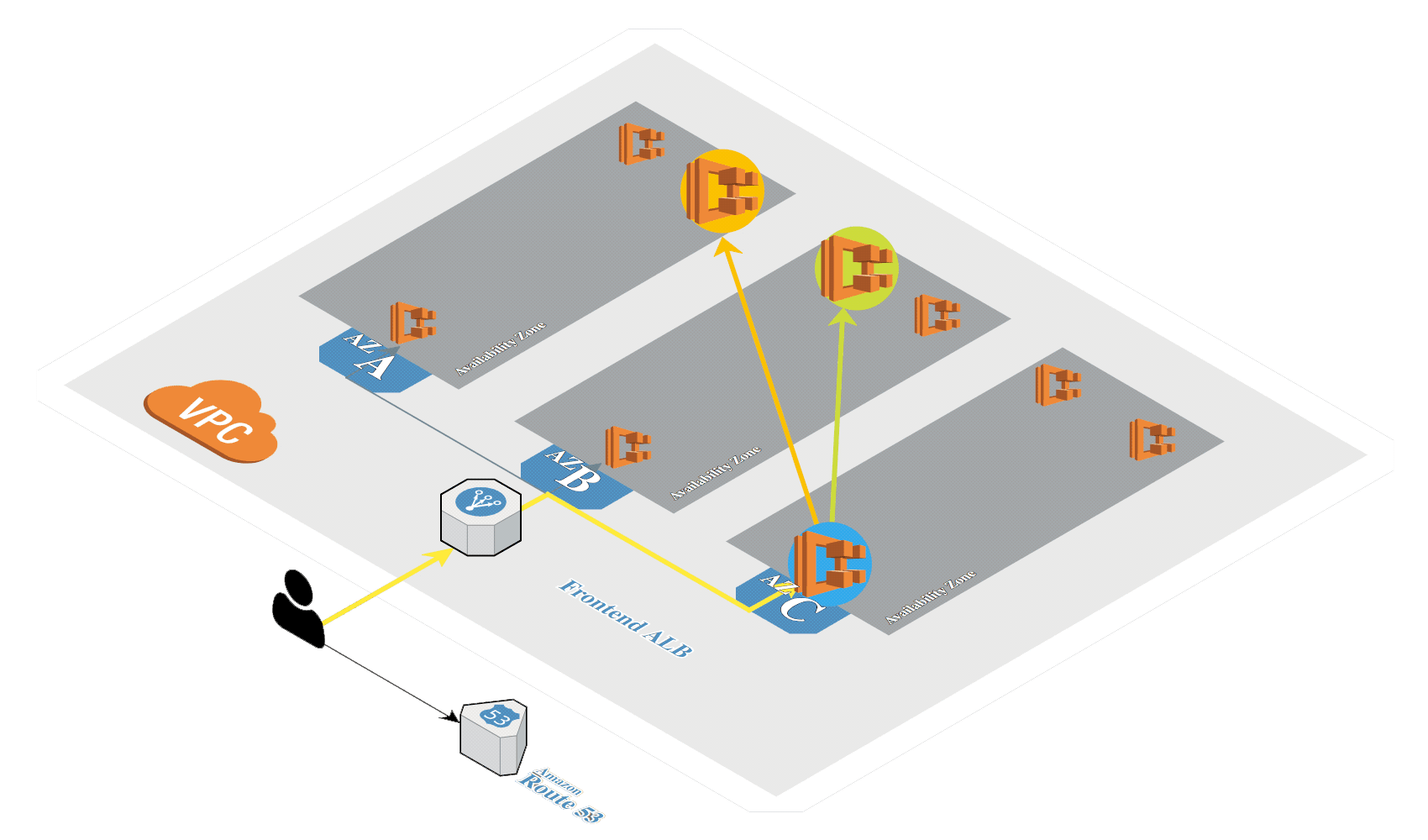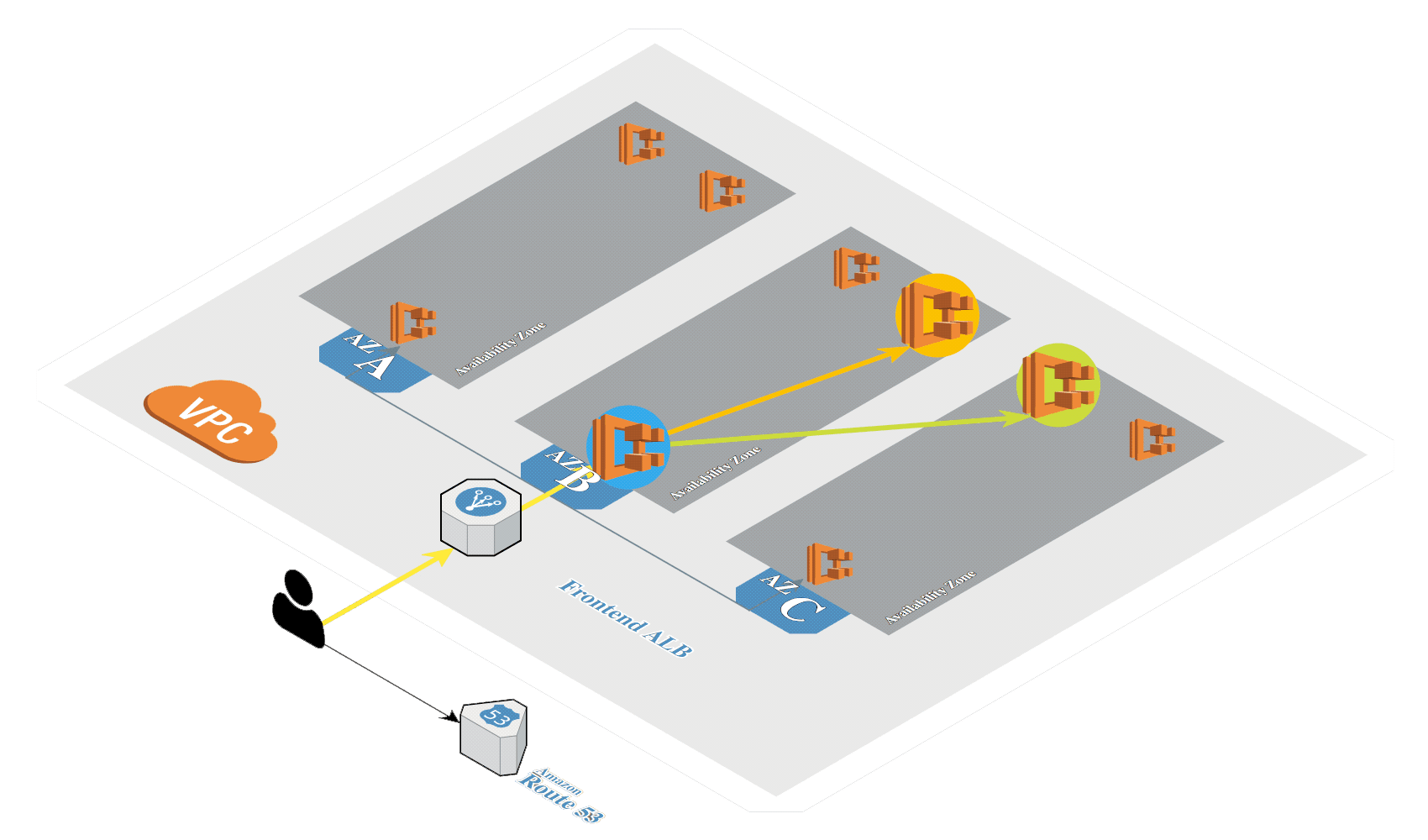
Create Amazon EKS in AWS by using eksctl.
Create the Amazon EKS cluster with Calico using eksctl:
cat > "tmp/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/eksctl-${CLUSTER_NAME}.yaml" << EOF
apiVersion: eksctl.io/v1alpha5
kind: ClusterConfig
metadata:
name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
region: ${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}
version: "1.22"
tags: &tags
karpenter.sh/discovery: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
$(echo "${TAGS}" | sed "s/ /\\n /g; s/^/ /g; s/=/: /g")
iam:
withOIDC: true
serviceAccounts:
- metadata:
name: cert-manager
namespace: cert-manager
wellKnownPolicies:
certManager: true
- metadata:
name: external-dns
namespace: external-dns
wellKnownPolicies:
externalDNS: true
karpenter:
# renovate: datasource=github-tags depName=aws/karpenter
version: 0.37.0
createServiceAccount: true
addons:
- name: vpc-cni
- name: kube-proxy
- name: coredns
- name: aws-ebs-csi-driver
managedNodeGroups:
- name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}-ng
amiFamily: Bottlerocket
instanceType: t3.medium
desiredCapacity: 2
minSize: 2
maxSize: 5
volumeSize: 30
tags:
<<: *tags
compliance:na:defender: bottlerocket
volumeEncrypted: true
EOF
if [[ ! -s "${KUBECONFIG}" ]]; then
if ! eksctl get clusters --name="${CLUSTER_NAME}" &> /dev/null; then
eksctl create cluster --config-file "tmp/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/eksctl-${CLUSTER_NAME}.yaml" --kubeconfig "${KUBECONFIG}"
else
eksctl utils write-kubeconfig --cluster="${CLUSTER_NAME}" --kubeconfig "${KUBECONFIG}"
fi
fi
aws eks update-kubeconfig --name="${CLUSTER_NAME}"
Add add the user or role to the aws-auth ConfigMap. This is handy if you are
using different user for CLI operations and different user/role for accessing
the AWS Console to see EKS Workloads in Cluster's tab.
if [[ -n ${AWS_CONSOLE_ADMIN_ROLE_ARN+x} ]] && ! eksctl get iamidentitymapping --cluster="${CLUSTER_NAME}" --arn="${AWS_CONSOLE_ADMIN_ROLE_ARN}" &> /dev/null; then
eksctl create iamidentitymapping --cluster="${CLUSTER_NAME}" --arn="${AWS_CONSOLE_ADMIN_ROLE_ARN}" --group system:masters --username admin
fi
if [[ -n ${AWS_USER_ROLE_ARN+x} ]] && ! eksctl get iamidentitymapping --cluster="${CLUSTER_NAME}" --arn="${AWS_USER_ROLE_ARN}" &> /dev/null; then
eksctl create iamidentitymapping --cluster="${CLUSTER_NAME}" --arn="${AWS_USER_ROLE_ARN}" --group system:masters --username admin
fi
Configure Karpenter
kubectl apply -f - << EOF
apiVersion: karpenter.sh/v1alpha5
kind: Provisioner
metadata:
name: ${CLUSTER_FQDN//./-}
spec:
requirements:
- key: karpenter.sh/capacity-type
operator: In
values: ["on-demand"]
- key: "topology.kubernetes.io/zone"
operator: In
values: ["${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}a", "${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}b", "${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}c"]
limits:
resources:
cpu: 1000
provider:
amiFamily: Bottlerocket
blockDeviceMappings:
- deviceName: /dev/xvda
ebs:
volumeSize: 3Gi
encrypted: true
- deviceName: /dev/xvdb
ebs:
volumeSize: 20Gi
encrypted: true
instanceProfile: eksctl-KarpenterNodeInstanceProfile-${CLUSTER_NAME}
subnetSelector:
karpenter.sh/discovery: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
securityGroupSelector:
karpenter.sh/discovery: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
tags:
Name: ${CLUSTER_FQDN}-karpenter
$(echo "${TAGS}" | sed "s/ /\\n /g; s/^/ /g; s/=/: /g")
ttlSecondsAfterEmpty: 30
EOF
Post installation tasks
Change TTL=60 of SOA + NS records for new domain (it can not be done in CloudFormation):
if [[ ! -s "tmp/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/route53-hostedzone-ttl.yml" ]]; then
HOSTED_ZONE_ID=$(aws route53 list-hosted-zones --query "HostedZones[?Name==\`${CLUSTER_FQDN}.\`].Id" --output text)
RESOURCE_RECORD_SET_SOA=$(aws route53 --output json list-resource-record-sets --hosted-zone-id "${HOSTED_ZONE_ID}" --query "(ResourceRecordSets[?Type == \`SOA\`])[0]" | sed "s/\"TTL\":.*/\"TTL\": 60,/")
RESOURCE_RECORD_SET_NS=$(aws route53 --output json list-resource-record-sets --hosted-zone-id "${HOSTED_ZONE_ID}" --query "(ResourceRecordSets[?Type == \`NS\`])[0]" | sed "s/\"TTL\":.*/\"TTL\": 60,/")
cat << EOF | jq > "tmp/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/route53-hostedzone-ttl.yml"
{
"Comment": "Update record to reflect new TTL for SOA and NS records",
"Changes": [
{
"Action": "UPSERT",
"ResourceRecordSet":
${RESOURCE_RECORD_SET_SOA}
},
{
"Action": "UPSERT",
"ResourceRecordSet":
${RESOURCE_RECORD_SET_NS}
}
]
}
EOF
aws route53 change-resource-record-sets --output json --hosted-zone-id "${HOSTED_ZONE_ID}" --change-batch="file://tmp/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/route53-hostedzone-ttl.yml"
fi
Install Kubernetes basic cluster components
cert-manager
Install cert-manager
helm chart
and modify the
default values.
Service account cert-manager was created by eksctl.
# renovate: datasource=helm depName=cert-manager registryUrl=https://charts.jetstack.io
CERT_MANAGER_HELM_CHART_VERSION="1.15.1"
helm repo add --force-update jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io
helm upgrade --install --version "${CERT_MANAGER_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace cert-manager --create-namespace --wait --values - cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager << EOF
installCRDs: true
serviceAccount:
create: false
name: cert-manager
extraArgs:
- --enable-certificate-owner-ref=true
EOF
Add ClusterIssuers for Let's Encrypt staging and production:
kubectl apply -f - << EOF
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-staging-dns
namespace: cert-manager
spec:
acme:
server: https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
email: ${MY_EMAIL}
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-staging-dns
solvers:
- selector:
dnsZones:
- ${CLUSTER_FQDN}
dns01:
route53:
region: ${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}
---
# Create ClusterIssuer for production to get real signed certificates
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-production-dns
namespace: cert-manager
spec:
acme:
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
email: ${MY_EMAIL}
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-production-dns
solvers:
- selector:
dnsZones:
- ${CLUSTER_FQDN}
dns01:
route53:
region: ${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}
EOF
kubectl wait --namespace cert-manager --timeout=10m --for=condition=Ready clusterissuer --all
external-dns
Install external-dns
helm chart
and modify the
default values.
external-dns will take care about DNS records.
Service account external-dns was created by eksctl.
# renovate: datasource=helm depName=external-dns registryUrl=https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
EXTERNAL_DNS_HELM_CHART_VERSION="6.38.0"
helm repo add --force-update bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
helm upgrade --install --version "${EXTERNAL_DNS_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace external-dns --wait --values - external-dns bitnami/external-dns << EOF
aws:
region: ${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}
domainFilters:
- ${CLUSTER_FQDN}
interval: 20s
policy: sync
serviceAccount:
create: false
name: external-dns
EOF
ingress-nginx
Install ingress-nginx
helm chart
and modify the
default values.
# renovate: datasource=helm depName=ingress-nginx registryUrl=https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
INGRESS_NGINX_HELM_CHART_VERSION="4.10.1"
helm repo add --force-update ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
helm upgrade --install --version "${INGRESS_NGINX_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace ingress-nginx --create-namespace --wait --values - ingress-nginx ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx << EOF
controller:
replicaCount: 2
watchIngressWithoutClass: true
service:
annotations:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-backend-protocol: tcp
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-type: nlb
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-additional-resource-tags: "$(echo "${TAGS}" | tr " " ,)"
EOF
Rancher
Create Let's Encrypt certificate (using Route53):
kubectl get namespace cattle-system &> /dev/null || kubectl create namespace cattle-system
kubectl apply -f - << EOF
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT}
namespace: cattle-system
spec:
secretName: ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT}
issuerRef:
name: letsencrypt-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT}-dns
kind: ClusterIssuer
commonName: "rancher.${CLUSTER_FQDN}"
dnsNames:
- "rancher.${CLUSTER_FQDN}"
EOF
kubectl wait --namespace cattle-system --for=condition=Ready --timeout=20m certificate "ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT}"
Prepare tls-ca-additional secret with Let's Encrypt staging certificate:
kubectl get -n cattle-system secret tls-ca &> /dev/null || kubectl -n cattle-system create secret generic tls-ca --from-literal=cacerts.pem="$(curl -sL https://letsencrypt.org/certs/staging/letsencrypt-stg-root-x1.pem)"
Install rancher-server
helm chart
and modify the
default values.
# renovate: datasource=helm depName=rancher registryUrl=https://releases.rancher.com/server-charts/latest
RANCHER_HELM_CHART_VERSION="2.8.5"
helm repo add --force-update rancher-latest https://releases.rancher.com/server-charts/latest
helm upgrade --install --version "v${RANCHER_HELM_CHART_VERSION}" --namespace cattle-system --wait --values - rancher rancher-latest/rancher << EOF
hostname: rancher.${CLUSTER_FQDN}
ingress:
tls:
source: secret
secretName: ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT}
privateCA: true
replicas: 1
bootstrapPassword: "${MY_PASSWORD}"
EOF
Clean-up
Install necessary software:
if command -v apt-get &> /dev/null; then
apt update -qq
DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -y -qq curl jq sudo unzip > /dev/null
fi
Install eksctl:
if ! command -v eksctl &> /dev/null; then
# renovate: datasource=github-tags depName=eksctl lookupName=weaveworks/eksctl
EKSCTL_VERSION="0.97.0"
curl -s -L "https://github.com/weaveworks/eksctl/releases/download/v${EKSCTL_VERSION}/eksctl_$(uname)_amd64.tar.gz" | sudo tar xz -C /usr/local/bin/
fi
Install AWS CLI binary:
if ! command -v aws &> /dev/null; then
# renovate: datasource=github-tags depName=awscli lookupName=aws/aws-cli
AWSCLI_VERSION="2.7.1"
curl -sL "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64-${AWSCLI_VERSION}.zip" -o "/tmp/awscli.zip"
unzip -q -o /tmp/awscli.zip -d /tmp/
sudo /tmp/aws/install
fi
Install kubectl binary:
if ! command -v kubectl &> /dev/null; then
# renovate: datasource=github-tags depName=kubernetes/kubectl extractVersion=^kubernetes-(?<version>.+)$
KUBECTL_VERSION="1.30.2"
sudo curl -s -Lo /usr/local/bin/kubectl "https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v${KUBECTL_VERSION}/bin/$(uname | sed "s/./\L&/g")/amd64/kubectl"
sudo chmod a+x /usr/local/bin/kubectl
fi
Set necessary variables and verify if all the necessary variables were set:
# AWS Region
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION="${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION:-eu-central-1}"
# Hostname / FQDN definitions
export CLUSTER_FQDN="${CLUSTER_FQDN:-mgmt1.k8s.use1.dev.proj.aws.mylabs.dev}"
export BASE_DOMAIN="${CLUSTER_FQDN#*.}"
export CLUSTER_NAME="${CLUSTER_FQDN%%.*}"
export KUBECONFIG="${PWD}/tmp/${CLUSTER_FQDN}/kubeconfig-${CLUSTER_NAME}.conf"
: "${AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID?}"
: "${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION?}"
: "${AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY?}"
: "${BASE_DOMAIN?}"
: "${CLUSTER_FQDN?}"
: "${CLUSTER_NAME?}"
: "${KUBECONFIG?}"
Remove EKS cluster and created components:
if eksctl get cluster --name="${CLUSTER_NAME}" 2> /dev/null; then
eksctl utils write-kubeconfig --cluster="${CLUSTER_NAME}" --kubeconfig "${KUBECONFIG}"
eksctl delete cluster --name="${CLUSTER_NAME}" --force
fi
Remove orphan EC2 created by Karpenter:
while read -r EC2; do
echo "Removing EC2: ${EC2}"
aws ec2 terminate-instances --instance-ids "${EC2}"
done < <(aws ec2 describe-instances --filters "Name=tag:kubernetes.io/cluster/${CLUSTER_NAME},Values=owned" Name=instance-state-name,Values=running --query "Reservations[].Instances[].InstanceId" --output text)
Remove orphan ELBs, NLBs (if exists):
# Remove Network ELBs
while read -r NETWORK_ELB_ARN; do
if [[ "$(aws elbv2 describe-tags --resource-arns "${NETWORK_ELB_ARN}" --query "TagDescriptions[].Tags[?Key == \`kubernetes.io/cluster/${CLUSTER_NAME}\`]" --output text)" =~ ${CLUSTER_NAME} ]]; then
echo "Deleting Network ELB: ${NETWORK_ELB_ARN}"
aws elbv2 delete-load-balancer --load-balancer-arn "${NETWORK_ELB_ARN}"
fi
done < <(aws elbv2 describe-load-balancers --query "LoadBalancers[].LoadBalancerArn" --output=text)
# Remove Classic ELBs
while read -r CLASSIC_ELB_NAME; do
if [[ "$(aws elb describe-tags --load-balancer-names "${CLASSIC_ELB_NAME}" --query "TagDescriptions[].Tags[?Key == \`kubernetes.io/cluster/${CLUSTER_NAME}\`]" --output text)" =~ ${CLUSTER_NAME} ]]; then
echo "💊 Deleting Classic ELB: ${CLASSIC_ELB_NAME}"
aws elb delete-load-balancer --load-balancer-name "${CLASSIC_ELB_NAME}"
fi
done < <(aws elb describe-load-balancers --query "LoadBalancerDescriptions[].LoadBalancerName" --output=text)
Remove Route 53 DNS records from DNS Zone:
CLUSTER_FQDN_ZONE_ID=$(aws route53 list-hosted-zones --query "HostedZones[?Name==\`${CLUSTER_FQDN}.\`].Id" --output text)
if [[ -n "${CLUSTER_FQDN_ZONE_ID}" ]]; then
aws route53 list-resource-record-sets --hosted-zone-id "${CLUSTER_FQDN_ZONE_ID}" | jq -c '.ResourceRecordSets[] | select (.Type != "SOA" and .Type != "NS")' |
while read -r RESOURCERECORDSET; do
aws route53 change-resource-record-sets \
--hosted-zone-id "${CLUSTER_FQDN_ZONE_ID}" \
--change-batch '{"Changes":[{"Action":"DELETE","ResourceRecordSet": '"${RESOURCERECORDSET}"' }]}' \
--output text --query 'ChangeInfo.Id'
done
fi
Remove CloudFormation stacks:
aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name "${CLUSTER_NAME}-route53"
Remove Volumes and Snapshots related to the cluster:
while read -r VOLUME; do
echo "Removing Volume: ${VOLUME}"
aws ec2 delete-volume --volume-id "${VOLUME}"
done < <(aws ec2 describe-volumes --filters "Name=tag:Cluster,Values=${CLUSTER_FQDN}" --query 'Volumes[].VolumeId' --output text)
while read -r SNAPSHOT; do
echo "Removing Snapshot: ${SNAPSHOT}"
aws ec2 delete-snapshot --snapshot-id "${SNAPSHOT}"
done < <(aws ec2 describe-snapshots --filter "Name=tag:Cluster,Values=${CLUSTER_FQDN}" --query 'Snapshots[].SnapshotId' --output text)
Wait for all CloudFormation stacks to be deleted:
aws cloudformation wait stack-delete-complete --stack-name "${CLUSTER_NAME}-route53"
aws cloudformation wait stack-delete-complete --stack-name "eksctl-${CLUSTER_NAME}-cluster"
Remove tmp/${CLUSTER_FQDN} directory:
rm -rf "tmp/${CLUSTER_FQDN}"
Clean-up completed:
echo "Cleanup completed..."
