SVN used for configuration management
Use Subversion over SSH to version-control Linux server configuration files
https://linux-old.xvx.cz/2010/03/svn-used-for-configuration-management/
Like every UNIX server admin, I’m using many various text-based configurations on my machines. It’s important to track “every” change of these important files to prevent problems with service stability.
I decided to set up Subversion server and store all useful configurations from my Linux boxes there. For this purpose I wrote script svnci which is used to save/delete/update files from svn. You can of course save all necessary files to SVN by hand, but it’s quicker to write a short parser for it.
The idea is to create the main repository “system_configs” where you will have subdirectories correspond to hostnames of your machines:
1
2
3
4
/var/lib/svn-repos/
└── system_configs
├── debian
└── czbrn0208
Then the access rights are set for each host to access the right directory in SVN. Then you should be able to commit changes to SVN using svn+ssh and private keys.
Use cron to automatically check changes in your files and add them to SVN.
Here is an example of how I installed subversion server on Debian and managed configuration files in it.
SVN server installation and configuration together with WebSVN
Install necessary software:
1
aptitude install openssh-server subversion websvn
Prepare SVN directory:
1
2
3
4
5
6
useradd svn
mkdir /home/svn
mkdir /home/svn/.ssh
mkdir /var/lib/svn-repos
chown -R svn:svn /home/svn
svnadmin create --fs-type fsfs /var/lib/svn-repos/system_configs
Now it’s necessary to set up access rights for servers which will read/write configuration to your SVN server. In my example I will use servers with hostnames debian and czbrn0208.
authz:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
cat >> /var/lib/svn-repos/system_configs/conf/authz << EOF
[/czbrn0208]
czbrn0208 = rw
[/debian]
debian = rw
EOF
svnserve.conf:
1
2
3
4
5
cat >> /var/lib/svn-repos/system_configs/conf/svnserve.conf << EOF
[general]
authz-db = authz
anon-access = none
EOF
Now you have to create directory structure matching the hostnames and import it to SVN:
1
2
3
mkdir -p /tmp/repo/debian /tmp/repo/czbrn0208
svn import /tmp/repo file:///var/lib/svn-repos/system_configs -m "Initial import ($(date +"%F %T"))"
rm -rf /tmp/repo
We should also change rights to svn user:
1
2
chmod -R g+w /var/lib/svn-repos/system_configs
chown -R svn:svn /var/lib/svn-repos
You should check your SVN directory structure and it should look like:
1
2
3
4
root@debian:/ svnlook tree /var/lib/svn-repos/system_configs
/
debian/
czbrn0208/
Now you need to add public keys to: /home/svn/.ssh/authorized_keys to allow access from hosts to SVN server using svn+ssh.
I include here also ssh key generation:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
root@debian:/ ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/root/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
e4:e7:b9:75:10:97:e4:4b:28:2d:ad:69:65:d2:3d:78 root@debian
The key's randomart image is:
+--[ RSA 2048]----+
| . |
| + * . |
| . + X E |
| o O = o |
| S = . . |
| + . . |
| o . . |
| o . |
| . |
+-----------------+
Now you should save $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa.pub to /home/svn/.ssh/authorized_keys like:
1
2
3
root@debian:/ echo "command=\"/usr/bin/svnserve -t -r /var/lib/svn-repos/system_configs \
--tunnel-user=`hostname`\",no-port-forwarding,no-pty,no-agent-forwarding,no-X11-forwarding \
`cat $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa.pub`" >> /home/svn/.ssh/authorized_keys
I should do the same for my second host czbrn0208, but I have to first transfer its public key to the server and then run a similar command:
1
2
3
4
5
6
root@debian:/ echo "command=\"/usr/bin/svnserve -t -r /var/lib/svn-repos/system_configs \
--tunnel-user=czbrn0208\",no-port-forwarding,no-pty,no-agent-forwarding,no-X11-forwarding \
`ssh root@czbrn0208 "cat /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"`" >> /home/svn/.ssh/authorized_keys
root@debian:/ cat /home/svn/.ssh/authorized_keys
command="/usr/bin/svnserve -t -r /var/lib/svn-repos --tunnel-user=debian",no-port-forwarding,no-pty,no-agent-forwarding,no-X11-forwarding ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEA7INCS6YC4VtsBpPa7H3sg4grSeRXSosWhWFzqyNDf++pau37DH1wZYCunfBpJjbiVMFJnOoT3LPmNc7DUTipEUAbz8p9XNt20qG8edLuf2zJ1VrqCxTydIJon+X+ZT6CI95v6/xG3SBevRKaV07kwzxIPdLMhJKdF0d7HKUOGTgWrWGIoRCnxSyIO5Jn7qEA+7/h7IYZo94IOedwDi1009akOfU73Iw/ArxtDAM752UNf7Y0gANtJRngBdT1nkiW1Yko2OPMG+gMDkc4bZ14TYqXzHeFHSGD/ipZlKn9czry3z5Pw5quI/K6m6uaWP9WuMC/CEjhRmNbOpsVRNg00Q== root@debian
command="/usr/bin/svnserve -t -r /var/lib/svn-repos/system_configs --tunnel-user=czbrn0208",no-port-forwarding,no-pty,no-agent-forwarding,no-X11-forwarding ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEA4p/ax75qZ5KiI1j3uy3rmgNFjyaxflKdVN0mQKPg4xzHAIy2cVdAk9eVdmNJOCKzjJej4dEL2NwgR0LDaaVJelZt2tI/GMZj4VnxLyAJQeJEeyMuUccwDJLF4X6CtUP22f7dzkHe6ovpRgBdUiuNWlmmOVkTwJqgQMp6P7c5BtKA60VLWvu1dfnChbJ8hay+9y890n893egOm6aAHpzbsaSPF0DxqrkNnVYrabOh4Y7HoXuKwJNdQtbR0zKdnURTk+GWMiUgyMU5NkEAC9GqAzVN/t+4NWZHDWuS1VlBdNbt1pmfMNhlUAIm/tsWtPdPwYEnI8MqolQHnHSDw9KYeQ== root@czbrn0208
Now you should be able to access SVN from the hosts:
1
2
3
4
root@debian:/ mkdir /root/configuration-`hostname`
root@debian:/ svn co svn+ssh://svn@debian.xvx.cz/`hostname` /root/configuration-`hostname`
root@czbrn0208:~ mkdir /root/configuration-`hostname`
root@czbrn0208:~ svn co svn+ssh://svn@debian.xvx.cz/`hostname` /root/configuration-`hostname`
Now your repositories are ready to import the first files/directories:
1
2
3
cp /etc/rc.local "/root/configuration-$(hostname)/"
svn add /root/configuration-debian/rc.local
svn ci --message "Test" /root/configuration-debian/
Now there should be the first file in the repository.
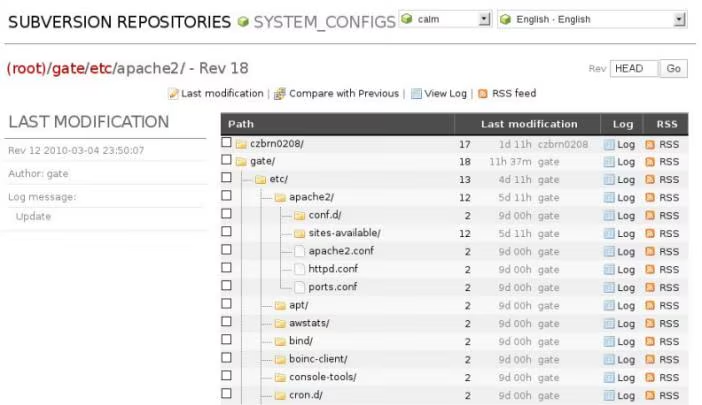
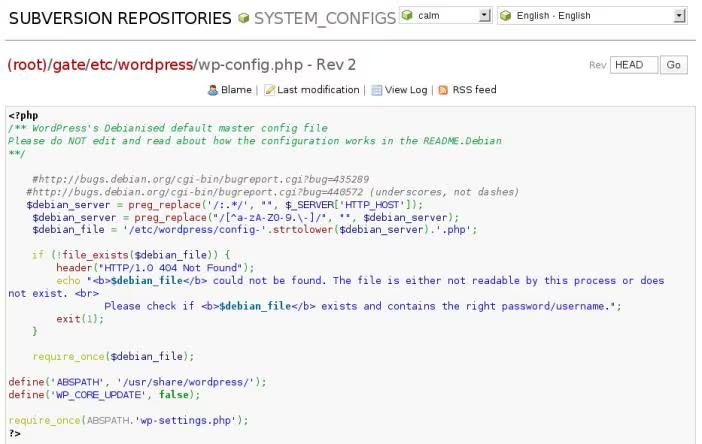
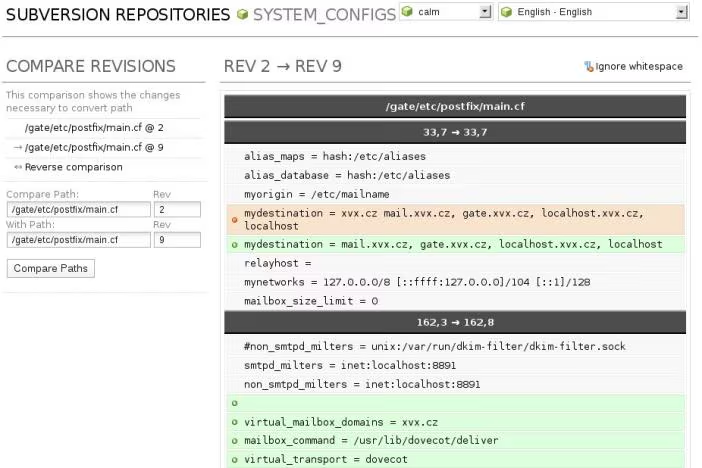
Now you can access your repository by WebSVN using https://my_server/websvn.
Everybody likes screenshots so I put there some from my own SVN server:
Script svnci
Here is a link for my script which can help you add/update/remove from the SVN repository without deep knowledge of it: svnci.
I use it because it’s faster and easier to remember than learning various SVN commands combined with shell - so here are some examples:
Add files to repository:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
gate:/etc/freeradius# svnci sql.conf
`/etc/freeradius/sql.conf' -> `/root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sql.conf'
A /root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sql.conf
Adding root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sql.conf
Sending root/configuration-gate/files
Transmitting file data ..
Committed revision 36.
Initial: /etc/freeradius/sql.conf
gate:/# svnci /etc/freeradius/sites-available/default
/etc/freeradius/sites-available -> /root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sites-available
`/etc/freeradius/sites-available/default' -> `/root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sites-available/default'
A /root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sites-available
A /root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sites-available/default
Adding root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sites-available
Adding root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sites-available/default
Sending root/configuration-gate/files
Transmitting file data ..
Committed revision 37.
Initial: /etc/freeradius/sites-available/default
Add directory to repository:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
gate:/etc# ls -ld cron.monthly
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 2010-02-25 17:02 cron.monthly
gate:/etc# svnci cron.monthly
/etc/cron.monthly -> /root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly
`/etc/cron.monthly/.placeholder' -> `/root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/.placeholder'
`/etc/cron.monthly/debsums' -> `/root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/debsums'
`/etc/cron.monthly/standard' -> `/root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/standard'
A /root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly
A /root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/.placeholder
A /root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/debsums
A /root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/standard
Adding root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly
Adding root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/.placeholder
Adding root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/debsums
Adding root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/standard
Sending root/configuration-gate/files
Transmitting file data ....
Committed revision 38.
Initial: /etc/cron.monthly/
Removing file(s):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
gate:/etc# cd cron.monthly
gate:/etc/cron.monthly# svnci -r debsums standard
Removing /etc/cron.monthly/debsums from repository: D /root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/debsums
Removing /etc/cron.monthly/standard from repository: D /root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/standard
Deleting root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/debsums
Deleting root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/standard
Sending root/configuration-gate/files
Transmitting file data .
Committed revision 39.
For updating files included in your repository you can use svnci -u command. It’s also handy to run it every night by cron to automatically track changes in your “monitored” files:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
gate:/etc# svnci -u
Sending configuration-gate/etc/apache2/httpd.conf
Sending configuration-gate/etc/apache2/sites-available/default-ssl
Sending configuration-gate/etc/munin/plugin-conf.d/munin-node
Sending configuration-gate/packages
Sending configuration-gate/root/bin/files
Transmitting file data .............
Committed revision 45.
Enjoy :-)