# Istio + Knative + cert-manager + kubed installation
Before we move on with other tasks it is necessary to install Nginx Ingress. It's also handy to install cert-manager for managing SSL certificates.
# Install cert-manager
cert-manager architecture:
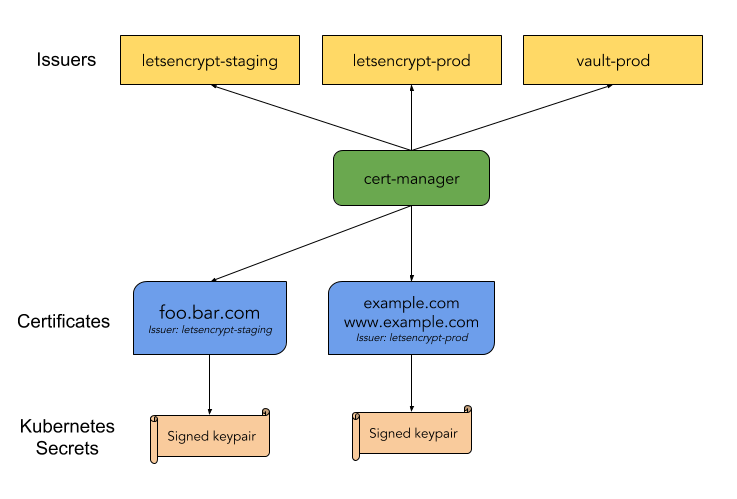
Install the CRDs resources separately:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jetstack/cert-manager/release-0.10/deploy/manifests/00-crds.yaml
sleep 5
Create the namespace for cert-manager and label it to disable resource validation:
kubectl create namespace cert-manager
kubectl label namespace cert-manager certmanager.k8s.io/disable-validation=true
Install the cert-manager Helm chart:
helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io
helm repo update
helm install cert-manager --namespace cert-manager --wait jetstack/cert-manager --version v0.10.1
Output:
"jetstack" has been added to your repositories
Hang tight while we grab the latest from your chart repositories...
...Successfully got an update from the "jetstack" chart repository
...Successfully got an update from the "stable" chart repository
Update Complete. ⎈ Happy Helming!⎈
NAME: cert-manager
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Dec 27 10:48:40 2019
NAMESPACE: cert-manager
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
cert-manager has been deployed successfully!
In order to begin issuing certificates, you will need to set up a ClusterIssuer
or Issuer resource (for example, by creating a 'letsencrypt-staging' issuer).
More information on the different types of issuers and how to configure them
can be found in our documentation:
https://docs.cert-manager.io/en/latest/reference/issuers.html
For information on how to configure cert-manager to automatically provision
Certificates for Ingress resources, take a look at the `ingress-shim`
documentation:
https://docs.cert-manager.io/en/latest/reference/ingress-shim.html
# Create ClusterIssuer for Let's Encrypt
Create ClusterIssuer for Route53 used by cert-manager. It will allow Let's
Encrypt to generate certificate. Route53 (DNS) method of requesting certificate
from Let's Encrypt must be used to create wildcard certificate *.mylabs.dev
(details here (opens new window)).

(https://b3n.org/intranet-ssl-certificates-using-lets-encrypt-dns-01/ (opens new window))
export USER_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY_BASE64=$(echo -n "$USER_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY" | base64)
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: aws-user-secret-access-key-secret
namespace: cert-manager
data:
secret-access-key: $USER_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY_BASE64
---
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-staging-dns
namespace: cert-manager
spec:
acme:
server: https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
email: petr.ruzicka@gmail.com
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-staging-dns
dns01:
providers:
- name: aws-route53
route53:
accessKeyID: ${USER_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID}
region: eu-central-1
secretAccessKeySecretRef:
name: aws-user-secret-access-key-secret
key: secret-access-key
---
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-production-dns
namespace: cert-manager
spec:
acme:
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
email: petr.ruzicka@gmail.com
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-production-dns
dns01:
providers:
- name: aws-route53
route53:
accessKeyID: ${USER_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID}
region: eu-central-1
secretAccessKeySecretRef:
name: aws-user-secret-access-key-secret
key: secret-access-key
EOF
# Generate TLS certificate
Create certificate using cert-manager:
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT}
namespace: cert-manager
spec:
secretName: ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT}
issuerRef:
kind: ClusterIssuer
name: letsencrypt-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT}-dns
commonName: "*.${MY_DOMAIN}"
dnsNames:
- "*.${MY_DOMAIN}"
acme:
config:
- dns01:
provider: aws-route53
domains:
- "*.${MY_DOMAIN}"
EOF
# Install kubed
It's necessary to copy the wildcard certificate across all "future" namespaces and that's the reason why kubed (opens new window) needs to be installed (for now). kubed (opens new window) can synchronize ConfigMaps/Secrets (opens new window) across Kubernetes namespaces/clusters.
Kubed - synchronize secret diagram:
Add kubed helm repository:
helm repo add appscode https://charts.appscode.com/stable/
helm repo update
Install kubed:
helm install kubed appscode/kubed --version 0.11.0 --namespace kube-system --wait \
--set apiserver.enabled=false \
--set config.clusterName=my_k8s_cluster
Output:
NAME: kubed
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Dec 27 10:49:39 2019
NAMESPACE: kube-system
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
To verify that Kubed has started, run:
kubectl --namespace=kube-system get deployments -l "release=kubed, app=kubed"
Annotate (mark) the cert-manager secret to be copied to other namespaces if necessary:
kubectl annotate secret ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT} -n cert-manager kubed.appscode.com/sync="app=kubed"
# Install Istio
Add Istio helm chart repository:
export ISTIO_VERSION="1.3.6"
helm repo add istio.io https://storage.googleapis.com/istio-release/releases/${ISTIO_VERSION}/charts/
helm repo update
Install CRDs for Istio:
kubectl create namespace istio-system
helm install istio-init istio.io/istio-init --wait --namespace istio-system --version ${ISTIO_VERSION}
kubectl -n istio-system wait --for=condition=complete job --all
Output:
namespace/istio-system created
NAME: istio-init
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Dec 27 10:49:56 2019
NAMESPACE: istio-system
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
job.batch/istio-init-crd-10-1.3.6 condition met
job.batch/istio-init-crd-11-1.3.6 condition met
job.batch/istio-init-crd-12-1.3.6 condition met
Label Istio namespace and which will trigger kubed to copy there the secret
with certificates signed by Let's Encrypt:
kubectl label namespace istio-system app=kubed
Install Istio:
(steps take from Knative page (opens new window))
helm install istio istio.io/istio --wait --namespace istio-system --version ${ISTIO_VERSION} \
--set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.autoscaleMax=1 \
--set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.autoscaleMin=1 \
--set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.ports[0].name=status-port \
--set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.ports[0].port=15020 \
--set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.ports[0].targetPort=15020 \
--set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.ports[1].name=http \
--set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.ports[1].nodePort=31380 \
--set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.ports[1].port=80 \
--set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.ports[1].targetPort=80 \
--set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.ports[2].name=https \
--set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.ports[2].nodePort=31390 \
--set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.ports[2].port=443 \
--set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.ports[3].name=ssh \
--set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.ports[3].nodePort=31400 \
--set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.ports[3].port=22 \
--set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.sds.enabled=true \
--set global.disablePolicyChecks=true \
--set global.k8sIngress.enableHttps=true \
--set global.k8sIngress.enabled=true \
--set global.proxy.autoInject=disabled \
--set grafana.datasources."datasources\.yaml".datasources[0].access=proxy \
--set grafana.datasources."datasources\.yaml".datasources[0].editable=true \
--set grafana.datasources."datasources\.yaml".datasources[0].isDefault=true \
--set grafana.datasources."datasources\.yaml".datasources[0].jsonData.timeInterval=5s \
--set grafana.datasources."datasources\.yaml".datasources[0].name=Prometheus \
--set grafana.datasources."datasources\.yaml".datasources[0].orgId=1 \
--set grafana.datasources."datasources\.yaml".datasources[0].type=prometheus \
--set grafana.datasources."datasources\.yaml".datasources[0].url=http://prometheus-system-np.knative-monitoring.svc.cluster.local:8080 \
--set grafana.enabled=true \
--set kiali.contextPath=/ \
--set kiali.createDemoSecret=true \
--set kiali.dashboard.grafanaURL=http://grafana.${MY_DOMAIN}/ \
--set kiali.dashboard.jaegerURL=http://jaeger.${MY_DOMAIN}/ \
--set kiali.enabled=true \
--set kiali.prometheusAddr=http://prometheus-system-np.knative-monitoring.svc.cluster.local:8080 \
--set mixer.adapters.prometheus.enabled=false \
--set pilot.traceSampling=100 \
--set prometheus.enabled=false \
--set sidecarInjectorWebhook.enableNamespacesByDefault=true \
--set sidecarInjectorWebhook.enabled=true \
--set tracing.enabled=true
Output:
NAME: istio
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Dec 27 10:50:54 2019
NAMESPACE: istio-system
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
Thank you for installing Istio.
Your release is named Istio.
To get started running application with Istio, execute the following steps:
1. Label namespace that application object will be deployed to by the following command (take default namespace as an example)
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled
kubectl get namespace -L istio-injection
2. Deploy your applications
kubectl apply -f <your-application>.yaml
For more information on running Istio, visit:
https://istio.io/
Let istio-ingressgateway to use cert-manager generated certificate via
SDS (opens new window).
Steps are taken from this URL: https://istio.io/docs/tasks/traffic-management/ingress/ingress-certmgr/ (opens new window).
kubectl -n istio-system patch gateway istio-autogenerated-k8s-ingress \
--type=json \
-p="[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/servers/1/tls", "value": {"credentialName": "ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT}", "mode": "SIMPLE", "privateKey": "sds", "serverCertificate": "sds"}}]"
Disable HTTP2 for gateway istio-autogenerated-k8s-ingress to be compatible
with Knative:
kubectl -n istio-system patch gateway istio-autogenerated-k8s-ingress --type=json \
-p="[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/servers/0/port", "value": {"name": "http", "number": "80", "protocol": "HTTP"}}]"
Allow the default namespace to use Istio injection:
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled
Configure the Istio services Jaeger (opens new window) and Kiali (opens new window) to be visible externally:
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: istio-services-gateway
namespace: istio-system
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway
servers:
- port:
number: 80
name: http-istio-services
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
- grafana-istio.${MY_DOMAIN}
- jaeger-istio.${MY_DOMAIN}
- kiali-istio.${MY_DOMAIN}
- port:
number: 443
name: https-istio-services
protocol: HTTPS
hosts:
- grafana-istio.${MY_DOMAIN}
- jaeger-istio.${MY_DOMAIN}
- kiali-istio.${MY_DOMAIN}
tls:
credentialName: ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT}
mode: SIMPLE
privateKey: sds
serverCertificate: sds
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: grafana-istio-virtual-service
namespace: istio-system
spec:
hosts:
- grafana-istio.${MY_DOMAIN}
gateways:
- istio-services-gateway
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: grafana.istio-system.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 3000
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: jaeger-istio-virtual-service
namespace: istio-system
spec:
hosts:
- jaeger-istio.${MY_DOMAIN}
gateways:
- istio-services-gateway
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: tracing.istio-system.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 80
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: kiali-istio-virtual-service
namespace: istio-system
spec:
hosts:
- kiali-istio.${MY_DOMAIN}
gateways:
- istio-services-gateway
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: kiali.istio-system.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 20001
EOF
# Create DNS records
Install external-dns (opens new window) and
let it manage mylabs.dev entries in Route 53 (Do not upgrade external-dns,
because it's not backward compatible and using different way of authentication
to Route53 using roles):
kubectl create namespace external-dns
helm install external-dns stable/external-dns --namespace external-dns --version 2.10.1 --wait \
--set aws.credentials.accessKey="${USER_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID}" \
--set aws.credentials.secretKey="${USER_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY}" \
--set aws.region=eu-central-1 \
--set domainFilters={${MY_DOMAIN}} \
--set istioIngressGateways={istio-system/istio-ingressgateway} \
--set interval="10s" \
--set policy="sync" \
--set rbac.create=true \
--set sources="{istio-gateway,service}" \
--set txtOwnerId="${USER}-k8s.${MY_DOMAIN}"
Output:
namespace/external-dns created
NAME: external-dns
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Dec 27 10:53:29 2019
NAMESPACE: external-dns
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
** Please be patient while the chart is being deployed **
To verify that external-dns has started, run:
kubectl --namespace=external-dns get pods -l "app.kubernetes.io/name=external-dns,app.kubernetes.io/instance=external-dns"
You should be able to reach these URLs:

