# Create k8s cluster
Before starting with the main content, it's necessary to provision the Kubernetes in AWS.
Use the MY_DOMAIN variable containing domain and LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT
variable.
The LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT variable should be one of:
staging- Let’s Encrypt will create testing certificate (not valid)production- Let’s Encrypt will create valid certificate (use with care)
export MY_DOMAIN=${MY_DOMAIN:-mylabs.dev}
export LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT=${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT:-staging}
echo "${MY_DOMAIN} | ${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT}"
# Prepare the local working environment
TIP
You can skip these steps if you have all the required software already installed.
Install necessary software:
if [ -x /usr/bin/apt ]; then
apt update -qq
DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -y -qq awscli curl docker.io gettext-base git jq openssh-client sudo wget > /dev/null
fi
Install kubectl (opens new window) binary:
if [ ! -x /usr/local/bin/kubectl ]; then
sudo curl -s -Lo /usr/local/bin/kubectl https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
sudo chmod a+x /usr/local/bin/kubectl
fi
Install kops (opens new window):
if [ ! -x /usr/local/bin/kops ]; then
curl -LO https://github.com/kubernetes/kops/releases/download/$(curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/kubernetes/kops/releases/latest | jq -r '.tag_name')/kops-linux-amd64
chmod +x kops-linux-amd64
sudo mv kops-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/kops
fi
Install kn client for Knative:
if [ ! -x /usr/local/bin/kn ]; then
sudo curl -s -L "https://github.com/knative/client/releases/download/v0.11.0/kn-linux-amd64" -o /usr/local/bin/kn
sudo chmod a+x /usr/local/bin/kn
fi
Install tkn client for Tekton:
if [ ! -x /usr/local/bin/tkn ]; then
curl -s -L https://github.com/tektoncd/cli/releases/download/v0.6.0/tkn_0.6.0_Linux_x86_64.tar.gz | tar xzf - -C /tmp/
sudo mv /tmp/tkn /usr/local/bin/
fi
Install hub (opens new window):
if [ ! -x /usr/local/bin/hub ]; then
curl -s -L https://github.com/github/hub/releases/download/v2.13.0/hub-linux-amd64-2.13.0.tgz | tar xzf - -C /tmp/
sudo mv /tmp/hub-linux-amd64-2.13.0/bin/hub /usr/local/bin/
fi
# Configure AWS
Authorize to AWS using AWS CLI: Configuring the AWS CLI (opens new window)
aws configure
...
Create DNS zone:
aws route53 create-hosted-zone --name ${MY_DOMAIN} --caller-reference ${MY_DOMAIN}
Use your domain registrar to change the nameservers for your zone (for example
mylabs.dev) to use the Amazon Route 53 nameservers. Here is the way how you
can find out the the Route 53 nameservers:
aws route53 get-hosted-zone --id $(aws route53 list-hosted-zones --query "HostedZones[?Name==\`${MY_DOMAIN}.\`].Id" --output text) --query "DelegationSet.NameServers"
Create policy allowing the cert-manager to change Route 53 settings. This will allow cert-manager to generate wildcard SSL certificates by Let's Encrypt certificate authority.
test -d tmp || mkdir tmp
envsubst < files/user_policy.json > tmp/user_policy.json
aws iam create-policy \
--policy-name ${USER}-k8s-${MY_DOMAIN} \
--description "Policy for ${USER}-k8s-${MY_DOMAIN}" \
--policy-document file://tmp/user_policy.json \
| jq
Output:
{
"Policy": {
"PolicyName": "pruzicka-k8s-mylabs.dev",
"PolicyId": "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
"Arn": "arn:aws:iam::822044714040:policy/pruzicka-k8s-mylabs.dev",
"Path": "/",
"DefaultVersionId": "v1",
"AttachmentCount": 0,
"PermissionsBoundaryUsageCount": 0,
"IsAttachable": true,
"CreateDate": "2019-12-27T09:41:14Z",
"UpdateDate": "2019-12-27T09:41:14Z"
}
}
Create user which will use the policy above:
aws iam create-user --user-name ${USER}-k8s-${MY_DOMAIN} | jq && \
POLICY_ARN=$(aws iam list-policies --query "Policies[?PolicyName==\`${USER}-k8s-${MY_DOMAIN}\`].{ARN:Arn}" --output text) && \
aws iam attach-user-policy --user-name "${USER}-k8s-${MY_DOMAIN}" --policy-arn $POLICY_ARN && \
aws iam create-access-key --user-name ${USER}-k8s-${MY_DOMAIN} > $HOME/.aws/${USER}-k8s-${MY_DOMAIN} && \
export USER_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=$(awk -F\" "/AccessKeyId/ { print \$4 }" $HOME/.aws/${USER}-k8s-${MY_DOMAIN}) && \
export USER_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=$(awk -F\" "/SecretAccessKey/ { print \$4 }" $HOME/.aws/${USER}-k8s-${MY_DOMAIN})
Output:
{
"User": {
"Path": "/",
"UserName": "pruzicka-k8s-mylabs.dev",
"UserId": "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
"Arn": "arn:aws:iam::822044714040:user/pruzicka-k8s-mylabs.dev",
"CreateDate": "2019-12-27T09:41:27Z"
}
}
The AccessKeyId and SecretAccessKey is need for creating the ClusterIssuer
definition for cert-manager.
# Create K8s in AWS
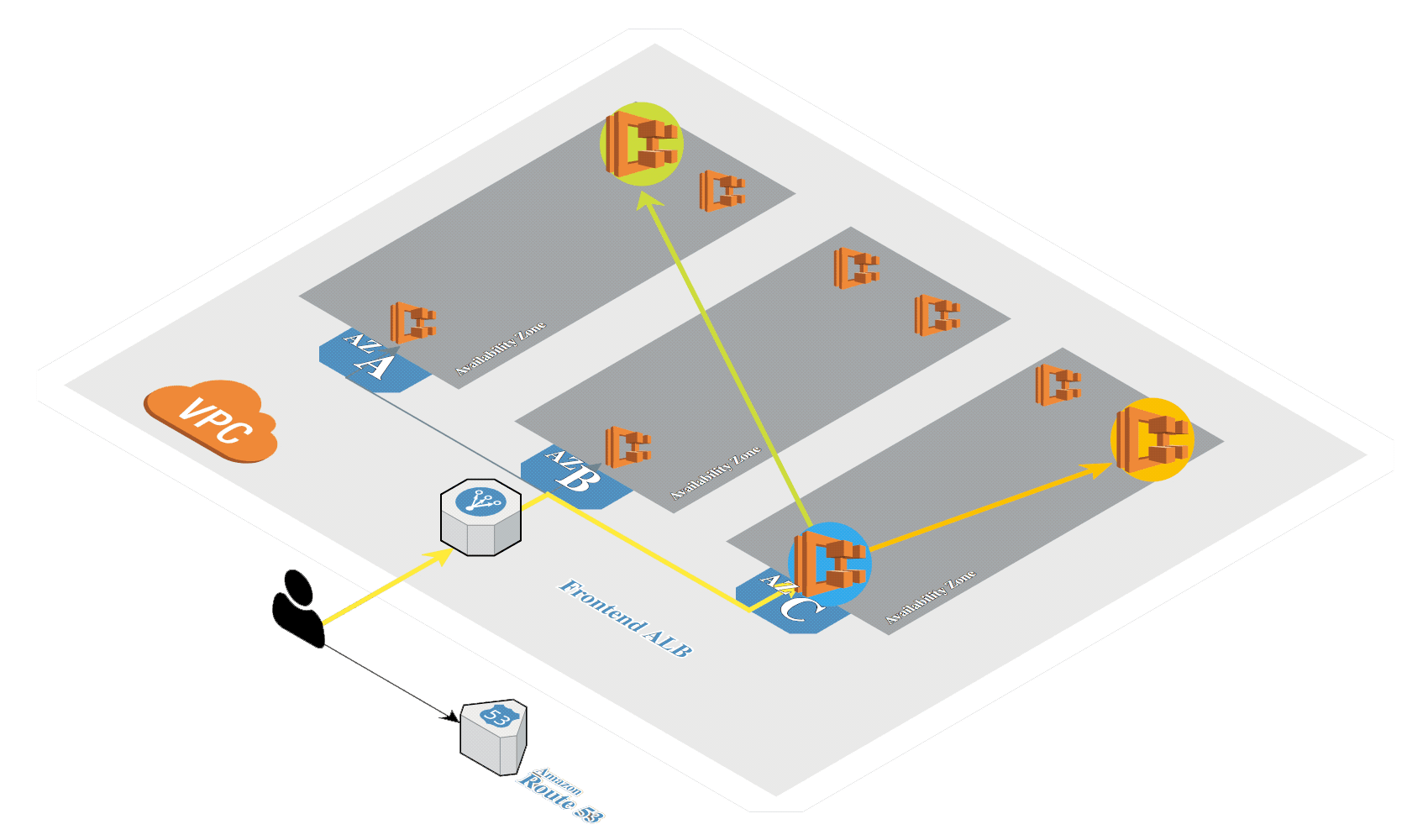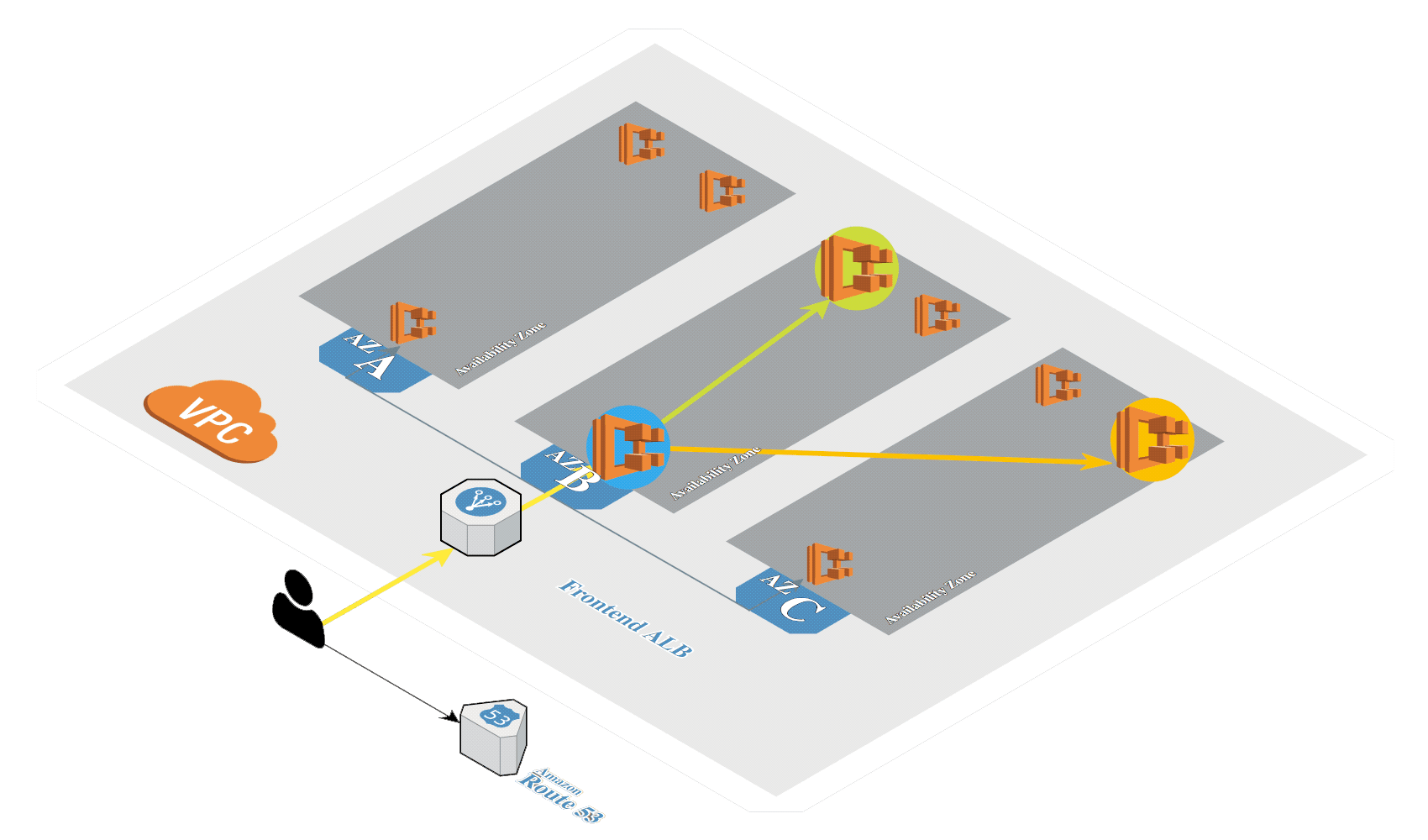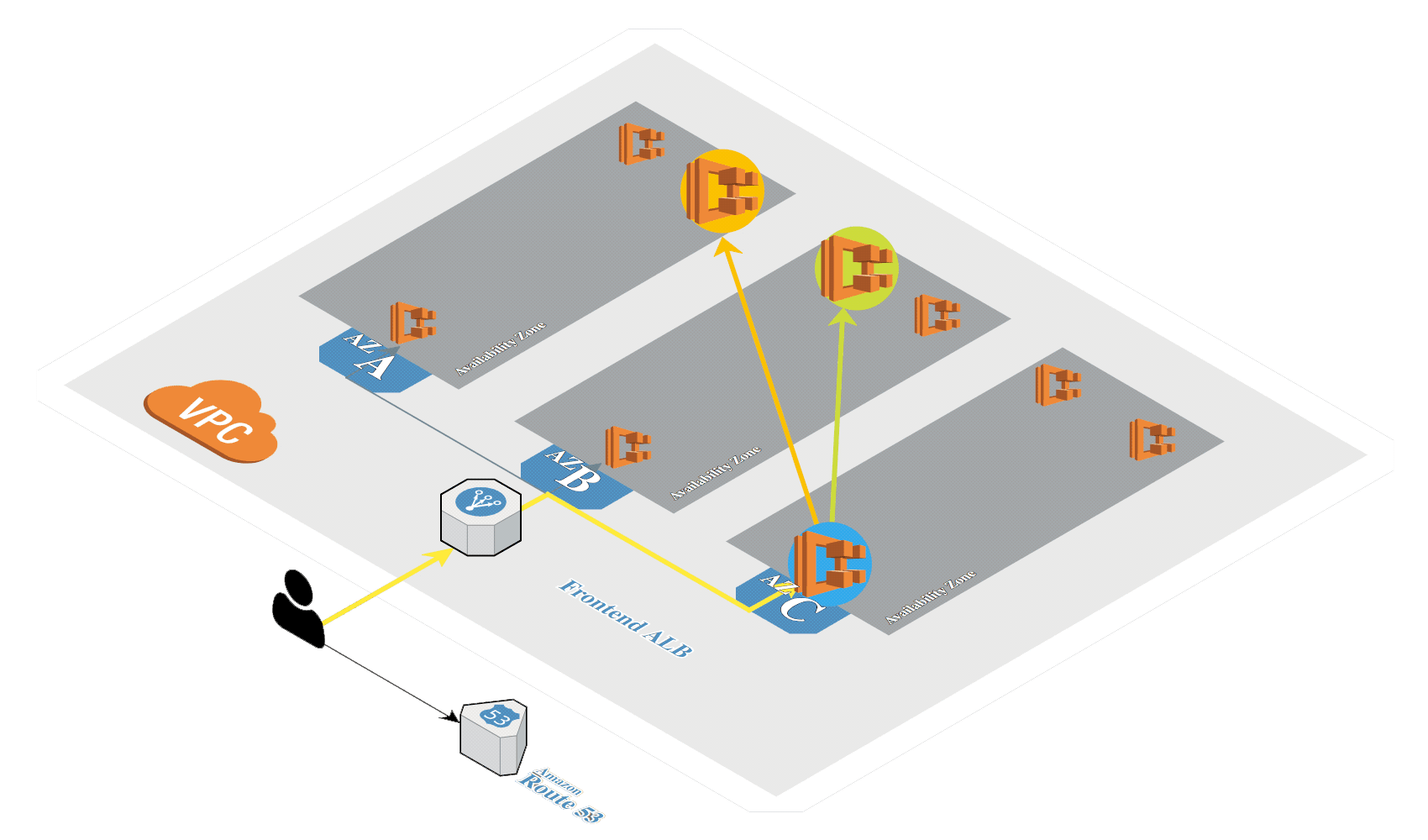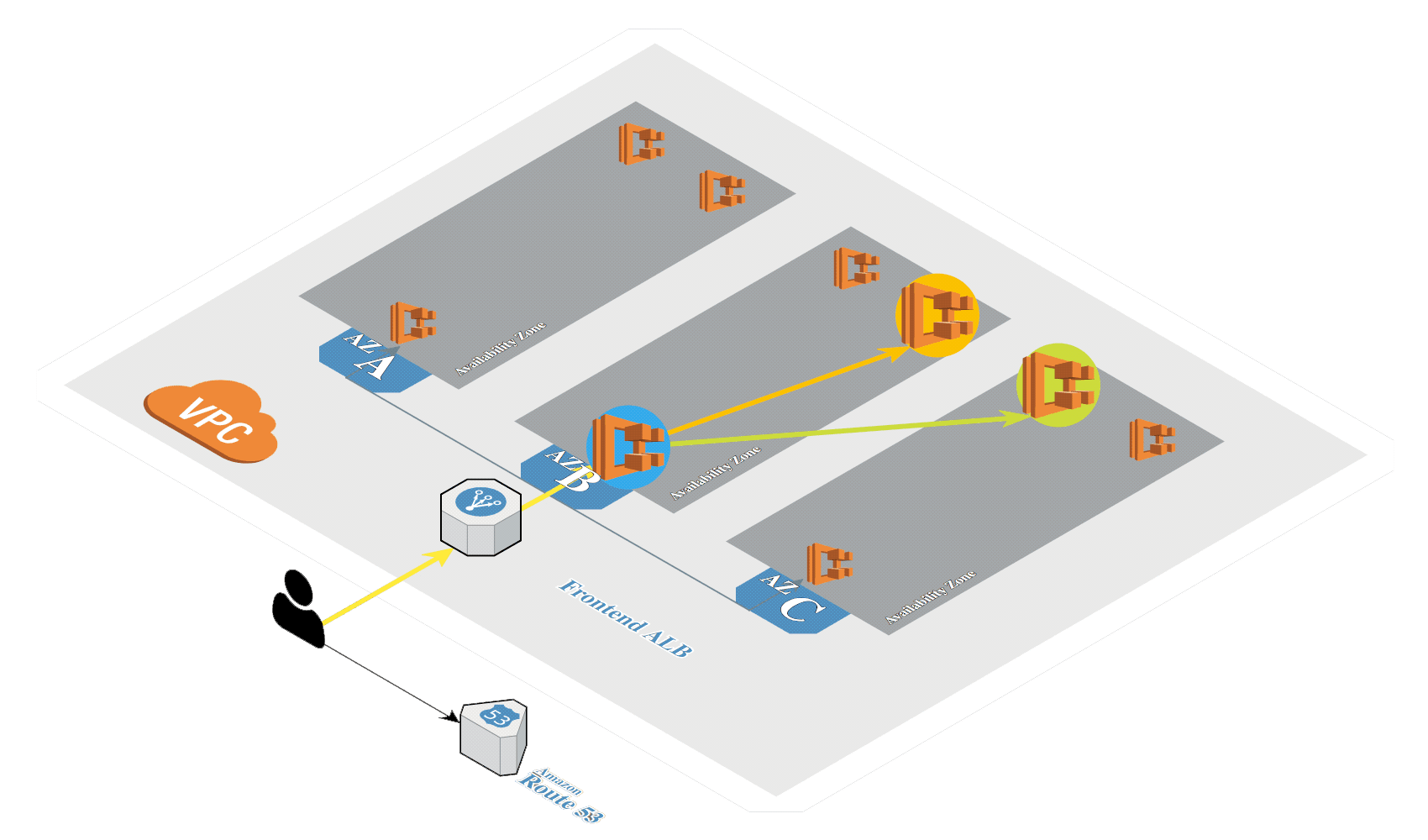
Generate SSH keys if not exists:
test -f $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa || ( install -m 0700 -d $HOME/.ssh && ssh-keygen -b 2048 -t rsa -f $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa -q -N "" )
Clone the k8s-knative-gitlab-harbor Git repository if it wasn't done already:
if [ ! -d .git ]; then
git clone --quiet https://github.com/ruzickap/k8s-k8s-knative-gitlab-harbor && cd k8s-knative-gitlab-harbor
fi
Create S3 bucket where the kops will store cluster status:
aws s3api create-bucket --bucket ${USER}-kops-k8s --region eu-central-1 --create-bucket-configuration LocationConstraint=eu-central-1 | jq
Output:
{
"Location": "http://pruzicka-kops-k8s.s3.amazonaws.com/"
}
Create Kubernetes cluster in AWS by using kops (opens new window):
kops create cluster \
--name=${USER}-k8s.${MY_DOMAIN} \
--state=s3://${USER}-kops-k8s \
--zones=eu-central-1a \
--networking=amazon-vpc-routed-eni \
--node-count=5 \
--node-size=t3.large \
--node-volume-size=20 \
--master-count=1 \
--master-size=t3.small \
--master-volume-size=10 \
--dns-zone=${MY_DOMAIN} \
--cloud-labels "Owner=${USER},Environment=Test,Division=Services" \
--ssh-public-key $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa.pub \
--yes
Output:
...
I1227 10:42:09.459809 15782 executor.go:103] Tasks: 91 done / 91 total; 0 can run
I1227 10:42:09.459901 15782 dns.go:155] Pre-creating DNS records
I1227 10:42:10.791005 15782 update_cluster.go:294] Exporting kubecfg for cluster
kops has set your kubectl context to pruzicka-k8s.mylabs.dev
Cluster changes have been applied to the cloud.
Changes may require instances to restart: kops rolling-update cluster
Wait for cluster to be up and running:
sleep 200
while `kops validate cluster --state=s3://${USER}-kops-k8s -o yaml 2>&1 | grep -q failures`; do sleep 5; echo -n .; done
echo
Store kubeconfig in current directory:
kops export kubecfg ${USER}-k8s.${MY_DOMAIN} --state=s3://${USER}-kops-k8s --kubeconfig kubeconfig.conf
Check if the new Kubernetes cluster is available:
export KUBECONFIG=$PWD/kubeconfig.conf
kubectl get nodes -o wide
Output:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
ip-172-20-37-106.eu-central-1.compute.internal Ready master 2m23s v1.15.6 172.20.37.106 35.159.31.183 Debian GNU/Linux 9 (stretch) 4.9.0-11-amd64 docker://18.6.3
ip-172-20-37-122.eu-central-1.compute.internal Ready node 56s v1.15.6 172.20.37.122 3.120.151.131 Debian GNU/Linux 9 (stretch) 4.9.0-11-amd64 docker://18.6.3
ip-172-20-37-204.eu-central-1.compute.internal Ready node 32s v1.15.6 172.20.37.204 18.196.187.216 Debian GNU/Linux 9 (stretch) 4.9.0-11-amd64 docker://18.6.3
ip-172-20-47-14.eu-central-1.compute.internal Ready node 67s v1.15.6 172.20.47.14 18.196.173.69 Debian GNU/Linux 9 (stretch) 4.9.0-11-amd64 docker://18.6.3
ip-172-20-47-61.eu-central-1.compute.internal Ready node 53s v1.15.6 172.20.47.61 18.184.73.151 Debian GNU/Linux 9 (stretch) 4.9.0-11-amd64 docker://18.6.3
ip-172-20-59-57.eu-central-1.compute.internal Ready node 83s v1.15.6 172.20.59.57 54.93.48.121 Debian GNU/Linux 9 (stretch) 4.9.0-11-amd64 docker://18.6.3
In case of using staging environment add "Let's Encrypt testing" fakelerootx1.pem (opens new window)
as trusted certificate authority:
wget -q https://letsencrypt.org/certs/fakelerootx1.pem -O tmp/fakelerootx1.pem
if [ ${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT} = "staging" ]; then
sudo mkdir -pv /etc/docker/certs.d/harbor.${MY_DOMAIN}/
sudo cp tmp/fakelerootx1.pem /etc/docker/certs.d/harbor.${MY_DOMAIN}/ca.crt
for EXTERNAL_IP in $(kubectl get nodes --output=jsonpath="{.items[*].status.addresses[?(@.type==\"ExternalIP\")].address}"); do
ssh -q -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -l admin ${EXTERNAL_IP} \
"sudo mkdir -p /etc/docker/certs.d/harbor.${MY_DOMAIN}/ && sudo wget -q https://letsencrypt.org/certs/fakelerootx1.pem -O /etc/docker/certs.d/harbor.${MY_DOMAIN}/ca.crt"
done
echo "*** Done"
fi