# Create k8s cluster
Before starting with the main content, it's necessary to provision the Kubernetes in Azure.
Use the MY_DOMAIN variable containing domain and LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT
variable.
The LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT variable should be one of:
staging- Let’s Encrypt will create testing certificate (not valid)production- Let’s Encrypt will create valid certificate (use with care)
export CLOUD_PLATFORM="${CLOUD_PLATFORM:-azure}"
if [ "$CLOUD_PLATFORM" = "aws" ]; then export MY_DOMAIN=${MY_DOMAIN:-mylabs.dev}; fi
if [ "$CLOUD_PLATFORM" = "azure" ]; then export MY_DOMAIN=${MY_DOMAIN:-myexample.dev}; fi
export LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT=${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT:-staging}
echo "*** ${CLOUD_PLATFORM} | ${MY_DOMAIN} | ${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT} ***"
# Prepare the local working environment
TIP
You can skip these steps if you have all the required software already installed.
Install necessary software and Azure CLI (opens new window):
if [ -x /usr/bin/apt ]; then
apt update -qq
DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -y -qq curl gettext-base git jq openssh-client sudo unzip wget > /dev/null
curl -L https://aka.ms/InstallAzureCLIDeb | bash
fi
Install kubectl (opens new window) binary:
if [ ! -x /usr/local/bin/kubectl ]; then
sudo curl -Lo /usr/local/bin/kubectl https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
sudo chmod a+x /usr/local/bin/kubectl
fi
Install hub (opens new window) binary:
if [ ! -x /usr/local/bin/hub ]; then
curl -L https://github.com/github/hub/releases/download/v2.12.4/hub-linux-amd64-2.12.4.tgz -o /tmp/hub-linux-amd64.tgz
tar xvzf /tmp/hub-linux-amd64.tgz hub-linux-amd64-2.12.4/bin/hub --strip-components 2
sudo mv hub /usr/local/bin/
fi
Install Terraform (opens new window):
if [ ! -x /usr/local/bin/terraform ]; then
curl -L https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/0.12.8/terraform_0.12.8_linux_amd64.zip -o /tmp/terraform_linux_amd64.zip
sudo unzip /tmp/terraform_linux_amd64.zip -d /usr/local/bin
rm /tmp/terraform_linux_amd64.zip
fi
Install Helm (opens new window):
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/master/scripts/get | bash -s -- --version v2.14.3
# Prepare the Azure environment
WARNING
These steps should be done only once
Create Service Principal and authenticate to Azure - this should be done only once for the new Azure accounts:
Azure Provider: Authenticating using a Service Principal with a Client Secret (opens new window)
Configure Terraform in Azure Cloud Shell with Bash (opens new window)
Login to the Azure CLI:
az login
Get Subscription ID for Default Subscription:
SUBSCRIPTION_ID=$(az account list | jq -r '.[] | select (.isDefault == true).id')
Create the Service Principal which will have permissions to manage resources in the specified Subscription:
az ad sp create-for-rbac --role="Contributor" --scopes="/subscriptions/$SUBSCRIPTION_ID" | jq
Output:
{
"appId": "axxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxx8",
"displayName": "azure-cli-2019-08-30-12-31-54",
"name": "http://azure-cli-2019-08-30-12-31-54",
"password": "dxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxx0",
"tenant": "5xxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxx8"
}
Login to Azure using Service Principal:
az login --service-principal -u axxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx -p dxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx --tenant 5xxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx | jq
Output:
[
{
"cloudName": "AzureCloud",
"id": "exxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxb",
"isDefault": true,
"name": "Pay-As-You-Go",
"state": "Enabled",
"tenantId": "5xxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxx8",
"user": {
"name": "axxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxx8",
"type": "servicePrincipal"
}
}
]
Verify the functionality by running:
az group list -o table
# Create DNS zone
WARNING
These steps should be done only once
See the details: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/dns/dns-delegate-domain-azure-dns (opens new window)
Create DNS resource group:
az group create --name ${AZURE_RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME}-dns --location ${AZURE_LOCATION}
Output:
{
"id": "/subscriptions/exxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxb/resourceGroups/pruzicka-k8s-test-dns",
"location": "westeurope",
"managedBy": null,
"name": "pruzicka-k8s-test-dns",
"properties": {
"provisioningState": "Succeeded"
},
"tags": null,
"type": null
}
Create DNS zone:
az network dns zone create -g ${AZURE_RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME}-dns -n ${MY_DOMAIN} | jq
Output
{
"etag": "0xxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxx1",
"id": "/subscriptions/exxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxb/resourceGroups/pruzicka-k8s-test-dns/providers/Microsoft.Network/dnszones/myexample.dev",
"location": "global",
"maxNumberOfRecordSets": 10000,
"name": "myexample.dev",
"nameServers": [
"ns1-06.azure-dns.com.",
"ns2-06.azure-dns.net.",
"ns3-06.azure-dns.org.",
"ns4-06.azure-dns.info."
],
"numberOfRecordSets": 2,
"registrationVirtualNetworks": null,
"resolutionVirtualNetworks": null,
"resourceGroup": "pruzicka-k8s-test-dns",
"tags": {},
"type": "Microsoft.Network/dnszones",
"zoneType": "Public"
}
List DNS nameservers for zone myexample.dev in Azure. You need to ask the
domain owner to delegate the zone myexample.dev to the Azure nameservers.
az network dns zone show -g ${AZURE_RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME}-dns -n ${MY_DOMAIN} -o json | jq
Output:
{
"etag": "00000002-0000-0000-7907-d16f315fd501",
"id": "/subscriptions/ef241c56-6f94-4aee-8861-9cd4ae74436b/resourceGroups/pruzicka-k8s-test-dns/providers/Microsoft.Network/dnszones/myexample.dev",
"location": "global",
"maxNumberOfRecordSets": 10000,
"name": "myexample.dev",
"nameServers": [
"ns1-06.azure-dns.com.",
"ns2-06.azure-dns.net.",
"ns3-06.azure-dns.org.",
"ns4-06.azure-dns.info."
],
"numberOfRecordSets": 2,
"registrationVirtualNetworks": null,
"resolutionVirtualNetworks": null,
"resourceGroup": "pruzicka-k8s-test-dns",
"tags": {},
"type": "Microsoft.Network/dnszones",
"zoneType": "Public"
}
This is what you should see inside the Azure Portal:
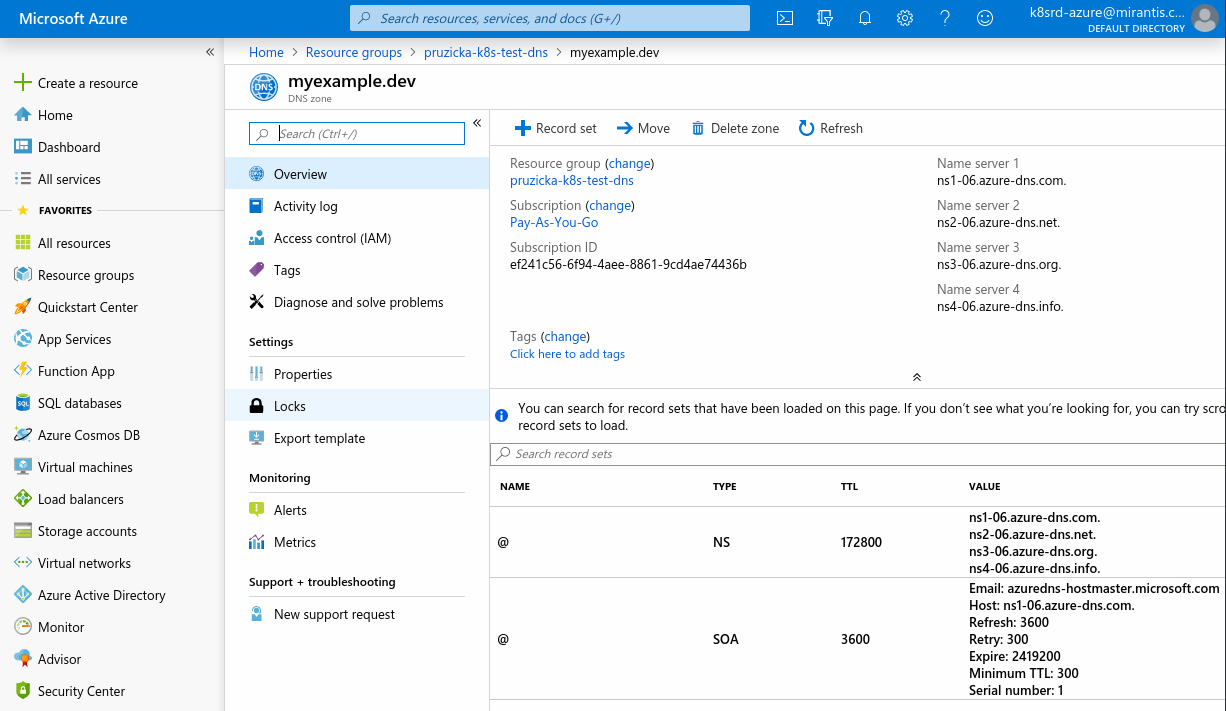
Check if DNS servers are forwarding queries to Azure DNS server:
dig +short -t SOA ${MY_DOMAIN}
Output:
ns1-06.azure-dns.com. azuredns-hostmaster.microsoft.com. 1 3600 300 2419200 300
# Create k8s in Azure
Generate SSH keys if not exists:
test -f $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa || ( install -m 0700 -d $HOME/.ssh && ssh-keygen -b 2048 -t rsa -f $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa -q -N "" )
Clone the k8s-sockshop Git repository if it wasn't done already:
if [ ! -d .git ]; then
git clone --quiet https://github.com/ruzickap/k8s-sockshop && cd k8s-sockshop
fi
Create the k8s cluster with applications:
cd terraform
./terraform.sh init
./terraform.sh plan
./terraform.sh apply -auto-approve
cd ..
Output:
...
Apply complete! Resources: 18 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
kubeconfig_export_command = 'export KUBECONFIG=$PWD/terraform/kubeconfig_pruzicka-k8s-myexample-dev'
Check if the new Kubernetes cluster is available:
export KUBECONFIG="$PWD/$(ls terraform/kubeconfig_*)"
kubectl get nodes -o wide
Output for Azure (AKS):
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
aks-pruzickak8s-34239724-0 Ready agent 7m30s v1.14.6 10.240.0.5 <none> Ubuntu 16.04.6 LTS 4.15.0-1052-azure docker://3.0.6
aks-pruzickak8s-34239724-1 Ready agent 7m37s v1.14.6 10.240.0.4 <none> Ubuntu 16.04.6 LTS 4.15.0-1052-azure docker://3.0.6
aks-pruzickak8s-34239724-2 Ready agent 7m23s v1.14.6 10.240.0.6 <none> Ubuntu 16.04.6 LTS 4.15.0-1052-azure docker://3.0.6
Output for AWS (EKS):
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
ip-10-0-1-116.eu-central-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 6m42s v1.13.10-eks-d6460e 10.0.1.116 18.184.43.220 Amazon Linux 2 4.14.138-114.102.amzn2.x86_64 docker://18.6.1
ip-10-0-2-250.eu-central-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 6m41s v1.13.10-eks-d6460e 10.0.2.250 54.93.247.34 Amazon Linux 2 4.14.138-114.102.amzn2.x86_64 docker://18.6.1
Verify if everything is working by accessing these URLs:
Azure:
AWS